COMBINE Study: Nelfinavir+Combivir vs. Nevirapine+Commbivir
Preliminary
Results of a Randomized Study Comparing Combivir plus Nevirapine or Nelfinavir
in Treatment-Na‘ve
The
COMBINE study is comparing a nevirapine regimen to a nelfinavir regimen, both
with combivir (AZT 300mg/3TC 150mg twice daily). Nelfinavir is dosed at 1250 mg
bid and nevirapine is dosed at 200 mg twice daily. This was a randomized, open, multicenter
trial in 12 hospitals in Spain and Argentina. 142 HIV-infected treatment-na‘ve
patients without AIDS defining illnesses were recruired between November 1998 to
August 1999. 38% acquired HIV through drug-use and 26% were women. Several
interesting substudies are ongoing but the data is not available yet: HIV-RNA in
reservoirs (tonsillar lymph tissue, CSF, semen); immunological changes, and
quality of life. At Retrovirus preliminary week 24 results were reported as the
study remains ongoing.
The
median baseline viral load was 65,000 copies/ml in the NFV arm, and 59,000
copies/ml in the NVP arm. 26 (37%) in the NFV arm and 21 (29%) in the NVP arm
had baseline viral load >100,000 copies/ml. Median CD4s were about 350 in
both arms. 20% had CD4s <200. The range in baseline viral load for the NFV
arm was 3200 to 1.6 million copies/ml. The range in the NVP arm was 1900 to
950,000 copies/ml.
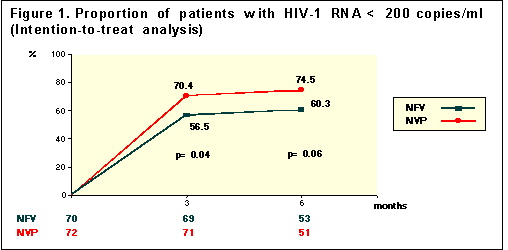
D Podzamczer and others reported the preliminary ITT results at week 24 which show 74% receiving NVP+combivir (n=51) had viral load <200 copies/ml, compared to 60% receiving nelfinavir+combivir (n=53)-- (p=0.06). ITT analysis (Intent-To-Treat, the more stringent form of analysis) at week 24 showed the NVP regimen had 58% <20 copies/ml (n=48) and 33% taking NFV regimen had <20 copies/ml (n=51)--(p=0.006).

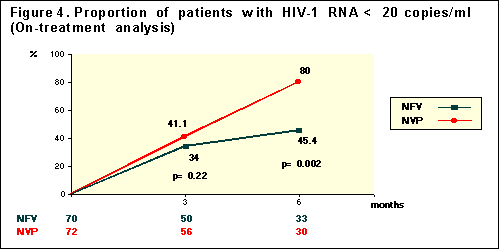
Using
the less stringent On-Treatment analysis at week 24, 91% receiving the NVP
regimen had <200 copies/ml (n=36), and 82% taking the NFV regimen had <200
copies/ml (n=34)--(p=0.12). 80% of those receiving NVP had <20 copies/ml
(n=30), and 45% taking NFV had <20 copies/ml (n=33)--(p=0.002). In general an
On-Treatment analysis looks only at people remaining on therapy. If a person
withdraws from study due to side effects, virologic failure, or lost to
follow-up for some reason, they are not included in this analysis. But in an
Intent-To-Treat analysis those individuals are counted as failures.
Using
an On-Treatment analysis, 100% (n=11) in the NVP arm had <200 copies/ml and
60% had <20 copies/ml. In the NFV arm 75% (n=16) had <200 copies/ml and
31% had <20 copies/ml.
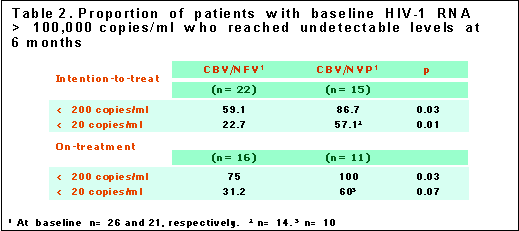
Looking at individuals with >100,000 copies/ml at baseline and using an ITT analysis, 86.7% in the NVP arm (n=15) had <200 copies/ml and 57% had <20 copies/ml. In the NFV arm (n=22) 59% had <200 copies/ml and 22.7% had <20 copies/ml.
At
week 24, CD4 increases were about 150 from baseline in both arms.
Patient Outcomes
About 33% stopped therapy in the study equally in both arms. In the NFV arm (n=25), 13 were lost to follow-up and 12 switched therapy due to intolerance (10), failure (1), and 1 was voluntary. In the NVP arm (n=23), 7 were lost to follow-up, and 14 switched therapy due to intolerance (14), failure (1), and 1 was voluntary. In the NFV arm, 7 of the 10 switches were due to GI symptoms, 1 ALT, 1 rash, and 1 neutropenia. In the NVP arm, 7 of the 14 switches were due to ALT elevations, 3 neutropenia, 2 rash, 1 GI symptom, 1 pending.