Increased Toxicity
Seen with Stavudine/Didanosine/Hydroxyurea in Treatment-Naive Patients
The dose of hydroxyurea
(HU) used was 600 mg bid (normal dose is 500 mg bid). In the na‘ve arm there
did not appear to be virologic benefit to adding HU. Interestingly, there was a
good deal of moderate-severe peripheral neuropathy reported in the na‘ve arms,
but not as much in the experienced arms. There also were more moderate-severe
amylase/lipase elevations in the na‘ve than the experienced arms. Adding HU
blunted the CD4 response even though HU was added 8 weeks after starting EFV/d4T/ddI.
There is a trend in the experienced patients for better virologic benefit when
HU was added compared to EF\/d4T/ddI alone (76% vs. 50% <50 copies/ml.
EFV+ddI+d4T was effective in the treatment na‘ve arm (ITT), at week 24: 73%
<50 copies/ml.
The lack of virologic
benefit in the na‘ve arm was when using d4T+ddI with HU. Using ddI+HU may be
different in terms of virologic benefit and toxicities.
Rob Murphy, MD, from
Northwestern University in Chicago, presented 48-week results from this study
whose purpose was to determine if adding hydroxyurea (HU) adds virologic benefit
to ddI, d4T and EFV. A second study purpose was to determine if prior experience
with nukes (except d4T and ddI) with or without a PI limits the virologic
response to the 3-drug regimen +HU combination. Also, the study was intended to
evaluate the safety and tolerability of this HU regimen. The patients were
required not to have a history of pancreatitis or any peripheral neuropathy.
A total of 98
treatment-naive and 47 treatment-experienced patients (who had received no prior
HU or NNRTI and less than 12 weeks of ddI or d4T) with CD4+ counts greater than
100 cells/mm3 and HIV RNA levels between 500 and 100,000 copies/mL, were
enrolled. In the na‘ve arm, the baseline median viral load was 46,000 copies/ml
in both the HU arm and the placebo arm. In the experienced group, the baseline
median viral load was 12,000 copies/ml in the HU arm and 6,300 in the placebo
arm. Across all 4 arms, baseline median CD4s were about the same 321-377.
The
treatment-experienced individuals were NNRTI and HU na‘ve. Prior PI therapy was
allowed. The HU dose was 600-mg bid which is higher than the standard dose of
500-mg bid. As well, ddI 400 mg once daily was used. There was a protocol
amendment 11/11/98 by which HU dose was reduced to 600/300 mg per day. If body
weight was <60 kg: d4T was dosed 30 mg bid, ddI was 300 mg once daily, and HU
was 600/300 mg per day. The study had been previously stopped by the its Data
and Safety Monitoring Board because of differences in toxicity seen in the 2
arms. HU or HU placebo was added 8 weeks after starting EFV+d4T+ddI.
Safety.
The study was stopped early due to excess toxicity, primarily peripheral
neuropathy, in the treatment-naive patients receiving HU. Among the naive
patients, 11 HU recipients of 47 (23%) enrolled in that arm stopped the study
due to toxicity, 8 (17%) because of peripheral neuropathy compared with 5 (10%)
in the placebo arm, 2 (4%) of whom had peripheral neuropathy. Among experienced
patients, 2 patients in the HU arm stopped therapy due to toxicity, both of whom
had peripheral neuropathy, and 3 in the placebo arm, 1 with peripheral
neuropathy. Grade 2 or 3 peripheral neuropathy was seen in 21 receiving HU vs. 9
receiving placebo among naive patients, and 11 HU vs. 3 placebo recipients among
experienced patients.
There was no difference
in moderate-severe amylase/lipase experience between the HU or placebo arms: 4
receiving HU in na‘ve group and 7 receiving placebo in na‘ve group were listed
as having "moderate-severe" amylase/lipase elevations, but only 1
person developed pancreatitis (in the placebo group), probably due to close
monitoring. In the experienced group, 3 receiving HU and 3 receiving placebo had
such amylase/lipase elevations (moderate-severe), and 1 in the HU group and 0 in
the placebo group had pancreatitis. In total there were 9 cases (6%), of
moderate-severe liver enzyme elevations: 2 in na‘ve HU group, 3 in na‘ve
placebo, 3 in experienced HU group, and 1 in experienced placebo group.
Time to the development
of peripheral neuropathy (grade 3; there was no reported grade 4) was
significantly faster in HU patients overall, and in the na‘ve group compared
with patients in the placebo group (P <0.02).
Antiviral
Activity & CD4s. In the na‘ve
group the individuals receiving HU did not appear to do better virologically
than those receiving placebo. Although the HU was added 8 weeks after starting
the triple regimen, the CD4 response was blunted in both the na‘ve and
experienced HU arms. In the na‘ve placebo arm CD4s increased 80 from baseline
at week 24 and 140 from baseline by week 48. While in the na‘ve HU arm, CD4s
did not increase at all at week 24 and by just 30 at week 48. The same CD4
response was seen in the experienced arms.
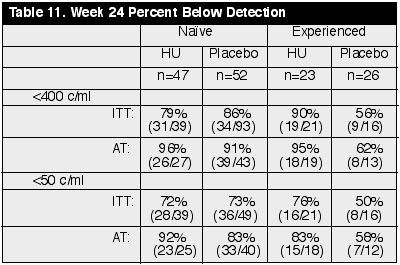
At week 24, in the
treatment-na‘ve arm by ITT, 79% (31/39) receiving HU (n=47) and 86% (42/49) in
placebo arm (n=52) had <400 copies/ml, about the same. By AT analysis, 96%
(26/27) on HU and 91% (39/43) on placebo had <400 copies/ml in the na‘ve
group. This reflects 18 discontinuations in the HU arm vs. 7 in the placebo arm.
By ITT at week 24, 72-73% had <50 copies/ml. in both arms. The 72% <50
copies/ml. result shows EFV+d4T+ddI was virologically effective. But by AT, 92%
in HU arm vs. 83% in placebo arm had <50 copies/ml. At week 48 by ITT, there
were about 85% <400 in both arms (n=26-33).
In the experienced arm at week 24 by ITT analysis, 90% (19/21) in the HU arm (n=23) and 56% (9/16) in the placebo arm (n=26) had <400 copies/ml. Using the AT analysis, 95% (18/19) in the HU arm and 62% (8/13) in the placebo arm had <400. In the <50 copies/ml analysis, 76% (16/21) in the HU arm and 50% (8/16) in the placebo arm had <50 copies/ml. And by AT analysis, 83% (15/18) in the HU arm, and 58% (7/12) in the placebo arm had <50 copies/ml. So, there is a trend for the HU arm to do better than placebo at week 24 in the experienced arm. The numbers of patients in the 48 week analysis in the experienced arm was very small: 4 in placebo and 11 in HU arms. (See Table 11)
