 |
 |
 |
| |
Tipranavir response in RESIST Stratified by Previous PI Use, & Baseline Viral Load & CD4 Count
|
| |
| |
Reported by Jules Levin
Patients in the RESIST studies were highly treatment experienced, with patients having used a median of 12 ARVs before entry into the trial. These patients also often had advanced disease, a high viral load and low CD4+ cell count. In the studies reported below, the researchers determine the efficacy of TPV/r compared with CPI/r as stratified by previous PI use, viral load and CD4+ cell count. I will report in next report on Tipranavir response for HCV/HBV cpinfected patients.
--This analysis reports the impact of previous PI use on Tipranavir Response
"24-Week Analysis of the Efficacy of Tipranavir Boosted With Ritonavir (TPV/r) in HIV Patients Stratified by Previous Protease Inhibitor (PI) Use"
Poster PE7.9/11
10th European AIDS Conference (EACS)
November 17-20, 2005
Dublin, Ireland
Jurgen Rockstroh1, J Villacian2, AM Quinson3, D Neubacher4, H Valdez4, D Mayers4
1Med. Universitätsklinik Bonn Allgemeine, Bonn, Germany; 2Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH, Ingelheim, Germany;
3Hopital de la Conception, Marseille, France; 4Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Ridgefield, CT
ABSTRACT
BACKGROUND
The Phase III RESIST trials demonstrated that TPV/r has a statistically superior efficacy over an optimized standard-of-care ritonavir-boosted comparator PI (CPI/r). This analysis reports the impact of previous PI use on various efficacy variables in HIV-1+ patients.
METHODS
Patient had ≥3-class ARV experience, including ≥2 PI-based regimens, one of which was the regimen at screening. Patients were randomized to receive TPV/r (500 mg/200 mg bid) or a preselected CPI/r together with an OBR. Treatment response (TR) was defined as a confirmed ≥1 log10 decrease in viral load from baseline.
Inclusion criteria:
≥18 years old
≥3 consecutive months of experience with all 3 classes of ARVs
≥2 PI-based regimens for at least 3 months, 1 of which was the current treatment regimen
Any CD4+ cell count was permissible
Viral load of ≥1000 copies/mL
≥1 primary protease mutation at 30N, 46I/L, 48V, 50V, 82A/F/L/T, 84V, 90M
≦2 mutations at codons 33, 82, 84, 90
Total cholesterol ≦400 mg/dL
Triglycerides ≦750 mg/dL
ALT ≦3.0 x ULN and AST ≦2.5 x ULN (≦DAIDS grade 1)
— Co-infected patients were only allowed to enroll if their screening
transaminases were ≦2.5-fold above the upper limit of normal or less
Because there were so few patients with either only 1 or 7 previously used PIs, these data were not included in the efficacy analysis.
RESULTS
1483 patients were randomized and treated, with 1159 patients (582 receiving TPV/r and 577 receiving CPI/r) available for analysis at week 24. The percentages of patients with both a TR and VL <400 copies/mL were greater in the TPV/r than CPI/r arm, with differences between arms increasing with increased PI experience:
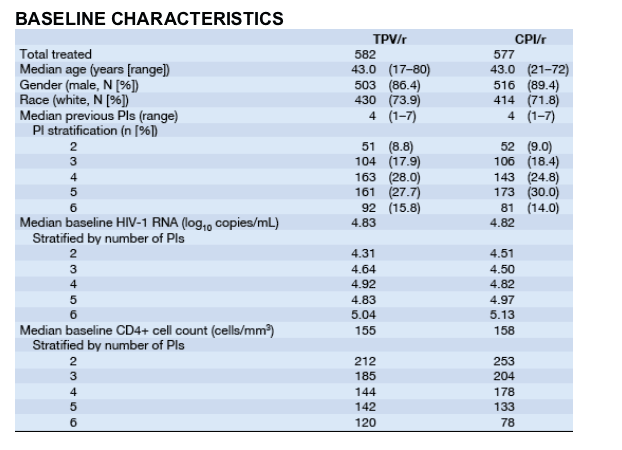
The overall treatment response (≥1 log10 reduction in 2 consecutive viral load measurements) for patients in the TPV/r arm was 41.2% (240/582) vs 21.3% (109/577) in the CPI/r arm
Patients in the TPV/r arm had a consistently improved treatment response compared to the CPI/r arm in all PI strata
Almost 50% of TPV/r patients with 3 or fewer previous PIs achieved a treatment response
The difference in treatment response became more dramatic as the PI experience of patients increased
--In those with 6 previous PIs, TPV/r had a 10 times greater treatment response than in CPI/r patients (38.0% [35/92] for TPV/r vs 3.7% [3/81] for CPI/r)
Approximately 40% of TPV/r patients presenting with 4 to 6 previous PIs at baseline achieved a treatment response
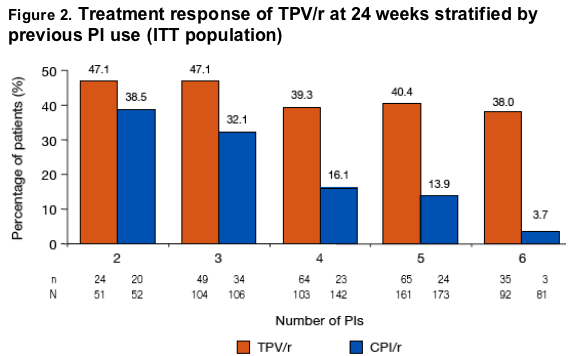
Overall, 34.2% (199/582) of TPV/r patients and 14.9% (86/577) of CPI/r patients had a viral load <400 copies/mL at 24 weeks
Overall, 23.9% (139/582) of TPV/r patients and 9.4 (54/577) of CPI/r patients had a viral load <50 copies/mL at 24 weeks
Consistent across all PI strata, more patients in the TPV/r arm had a viral load <400 copies/mL and <50 copies/mL at 24 weeks
Almost 45% of patients with 3 or fewer previous PIs had viral loads <400 copies/mL at 24 weeks
-- In patients with 3 previously used PIs, almost twice the percentage of patients in the TPV/r arm had a viral load <50 copies/mL than in the CPI/r arm (32.7% [34/104] vs 17.0% [18/106])
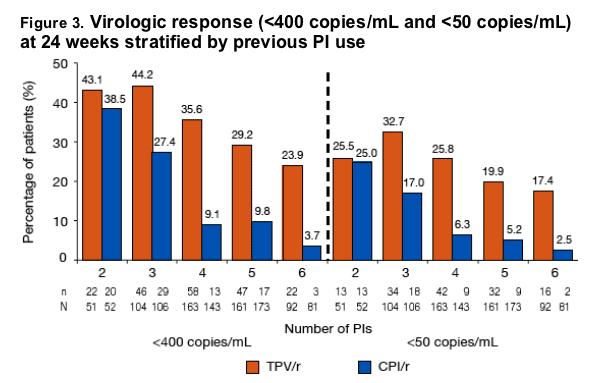
The superior response of TPV/r is also reflected in CD4+ cell count, VL <50 copies/mL, and absolute viral load.
CONCLUSION
At any given level of PI experience, TPV/r provided a superior treatment efficacy over CPI/r, and increased with increasing PI experience. However, patients starting TPV/r earlier had better overall treatment outcomes at 24 weeks.
Tipranavir Response in RESIST by Viral Load & CD4 Count
"Superior Efficacy of Tipranavir Boosted With Ritonavir (TPV/r) vs Comparator Boosted Protease Inhibitors (CPI/r) in Patients Stratified by Viral Load (VL) and CD4+ Cell Count'
Poster PE7.3/22
10th European AIDS Conference (EACS)
November 17-20, 2005
Dublin, Ireland
Charles Farthing, MD, for the RESIST Study Teams
AIDS Healthcare Foundation, Los Angeles, CA, USA
ABSTRACT
BACKGROUND
The pivotal Phase III RESIST trials demonstrated the statistically superior efficacy of TPV/r over an optimized standard-of-care CPI/r at 24 weeks. Here we assessed the treatment response of TPV/r and CPI/r at different baseline VL and CD4+ cell-count stratifications.
METHODS
Patients with experience on 2 different PI regimens, documented PI resistance, and a VL ≥1000 copies/mL were eligible; there were no CD4+ cell-count restrictions. Patients were randomized to either TPV/r (500 mg/200 mg bid) or a preselected CPI/r, and all patients received an optimized background regimen. Treatment response was defined as a confirmed ≥1 log10 decrease in VL from
baseline.
RESULTS
1483 patients were randomized and treated, and 1159 patients (582 in the TPV/r arm and 577 in the CPI/r arm) were available for analysis at Week 24. Median baseline VL was 4.83 log10 copies/mL and 4.82 log10 copies/mL; median baseline CD4+ cell counts were 155 cells/mm3 and 158 cells/mm3 in the TPV/r and CPI/r arms, respectively. Patients on TPV/r had a superior treatment response and larger median VL reductions than CPI/r patients in all VL strata: ≦10,000 copies/mL, TPV/r 56.0% and 1.7 log10 vs CPI/r 31.1% and 0.5 log10; >10,000-100,000 copies/mL, TPV/r 41.7% and 0.7 log10 vs CPI/r 19.4% and 0.2 log10; >100,000 copies/mL, TPV/r 34.9% and 0.6 log10 vs CPI/r, 13.7% and
0.2 log10.
Similarly, treatment response with TPV/r was superior to CPI/r in all CD4+ cell-count strata: >350 cells/mm3, TPV/r 46% vs CPI/r 21.2%; 201-350 cells/mm3, TPV/r 44.4% vs CPI/r 23.9%; 50-200 cells/mm3 TPV/r 46.5% vs CPI/r 21.2%; and <50 cells/mm3 TPV/r 26.3% vs CPI/r 9.5%.
CONCLUSION
TPV/r provided superior efficacy to CPI/r, regardless of baseline VL and CD4+ cell count. In these treatment-experienced patients, there was a good treatment response with TPV/r in patients with high and low baseline VLs.
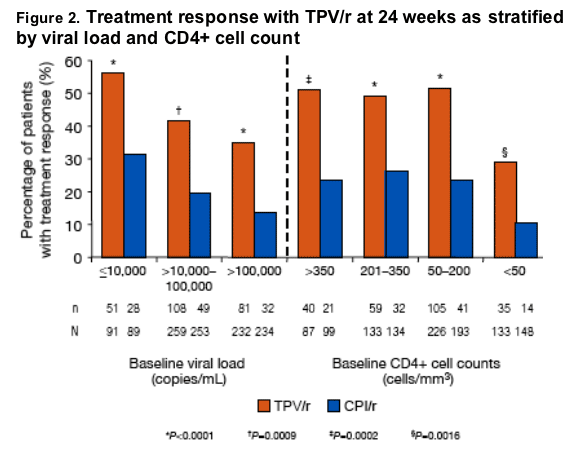
The overall treatment response (≥1 log10 decrease in viral load) was 41.2%
(240/582) for TPV/r vs 18.9% (109/577) for CPI/r (P<0.0001)
TPV/r provided a superior treatment response compared with CPI/r at both high
(>100,000 copies/mL [34.9% vs 13.7%]) and low (≦10,000 copies/mL [56.0% vs
31.1%]) baseline viral loads
Treatment response with TPV/r was superior to CPI/r in all CD4+ cell-count strata
--The treatment response for TPV/r was more than twice that for CPI/r at baseline CD4+ cell counts of >350 copies/mL (46.0% vs 21.2%) and almost three times that of CPI/r at <50 copies/mL (26.3% vs 9.5%)
--An improved treatment response was seen in TPV/r patients with decreased CD4+ cell counts compared with CPI/r patients
EFFICACY: CHANGE IN VIRAL LOAD BY BASELINE STRATIFICATION
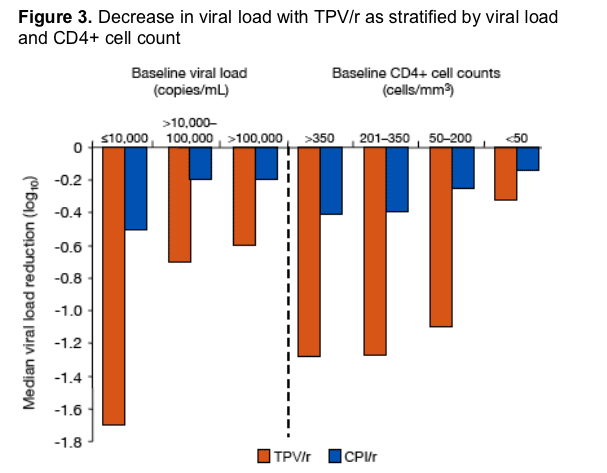
The overall median decrease in viral load was 0.80 log10 for TPV/r vs 0.25 log10 for CPI/r (P<0.0001)
TPV/r patients had a greater decrease in viral load at all baseline viral load
stratifications than did those in the CPI/r arm
TPV/r patients had a greater reduction in viral load than CPI/r patients at all baseline CD4+ cell counts
The decrease in viral load was relatively stable for patients with baseline CD4+ cell counts of 50 to >350 cells/mm3 (-1.27 log10 to -1.09 log10)
--Virologic response was reduced at low CD4+ cell counts in the TPV/r arm, although it was still superior to that of the CPI/r arm
|
|
| |
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|