 |
 |
 |
| |
Metabolic Analyses within A5095: Effect of Efavirenz against an All-nucleoside/Nucleotide Background: 3 Nukes; TDF Regimen vs EFV Regimens
|
| |
| |
Cecilia Shikuma, Univ of Hawaii, Honolulu, US; AIDS Clin Trials Group A5095 Study Team
Limited prospective data exist on the metabolic effects of protease inhibitor (PI)-sparing regimens when used as initial treatment for HIV. We report on fasting metabolic and body composition changes seen in 1147 treatment-naive subjects who initiated such regimens.
Week-0 to -24 changes in fasting metabolic (triglyceride [TG] and total [T-C], LDL [LDL-C], and HDL [HDL-C] cholesterol, lactate, glucose, insulin resistance by homeostasis model assessment [HOMA]) and anthropometric indices (waist, hip, and arm circumferences) were compared in subjects randomized to the 3 arms of ACTG 5095: zidovudine/lamivudine/abacavir (ZDV/3TC/ABC) vs ZDV/3TC + efavirenz (EFV) vs ZDV/3TC/ABC + EFV. Changes from weeks 0 to 96 were assessed in the 2 EFV-containing arms.
The ZDV/3TC/ABC arm was discontinued early because of a higher rate of virologic failure, and patients with HIV RNA <200 copies/mL were offered randomization to intensify their regimen with either EFV or TDF (occurred after week 24). Metabolic changes from this new baseline at week 24 to week 96 were compared between the EFV vs TDF arms. Kruskal-Wallis test was used for comparing between-group differences in continuous outcomes.
Results
From wk 0-24, median changes (mg/dL; intent-to-treat) in the ZDV/3TC/ABC, ZDV/3TC + EFV and ZDV/3TC/ABC + EFV arms, respectively, were: TG (-1,7,18); T-C (5, 23, 29); LDL-C (1, 9, 14); HDL-C (5, 10, 10), lactate (1.3, 1.5, 1.4) and glucose (5, 6, 6), with median increases in log (HOMA IR) of 0.26, 0.13, 0.19 (p <0.05 for all except TG and LDL changes in the ZDV/3TC/ABC arm.
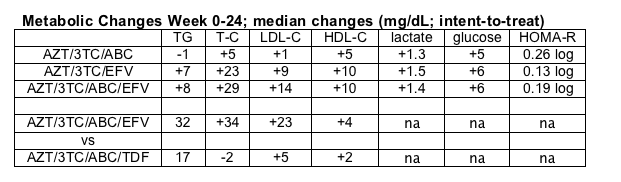
Similar values were seen in the as-treated analyses.
By intent to treat, T-C, LDL-C, and HDL-C values were higher in both EFV-containing arms than in the ZDV/3TC/ABC arm (p <0.001).
Anthropometric changes were not different among arms (p >0.09).
No consistent differences were noted with the addition of ABC to ZDV/3TC/EFV from week 0 to 24 or from week 0 to 96.
Following randomization to EFV vs TDF in the original ZDV/3TC/ABC arm, median changes from week 24 to 96 in T-C, LDL-C, and HDL-C were higher in the EFV vs TDF arm: T-C (34, -2); LDL-C (23, 5); and HDL-C (4, -2) (intent to treat, p ≦0.001); TG changes were similar (32, 17).
The authors concluded that over the course of the study, minimal to modest changes were seen in all assessed metabolic parameters except 0- to 24-week TG and LDL changes in the ZDV/3TC/ABC arm. Compared to all nucleoside/nucleotide-based regimens, the inclusion of EFV was associated with higher LDL-C, as well as higher HDL-C levels. No consistent metabolic effect was noted with the addition of ABC to ZDV/3TC/EFV.
|
|
| |
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|