 |
 |
 |
| |
48-week analysis of LPV/r monotherapy compared to LPV/r + AZT/3TC in antiretroviral-naive patients: MONARK trial
|
| |
| |
JF Delfraissy, P Flandre, C Delaugerre, A Horban,
PM Girard, C Rouzioux, M Norton, I Cohen Codar,
P NgoVan, JP Chauvin
Thursday Late Breaker Oral Presentation #LB202
Reported by Jules Levin
XVI Intl AIDS Conference, Toronto, Aug 17, 2006
MONARK Study Design and Baseline Characteristics
Entry criteria
-- Antiretroviral naive
-- HIV-1 RNA <100,000 c/mL
-- CD4 > 100 cells/mm3
Baseline characteristics: Mean (range)
-- HIV-1 RNA (log10 c/mL):4.39 (1.70-5.87; mono) vs 4.34 (2.85-5.36; Triple)
-- CD4 (cell/mL): 257 (86-1247; mono) vs 234 (106-521; Triple)
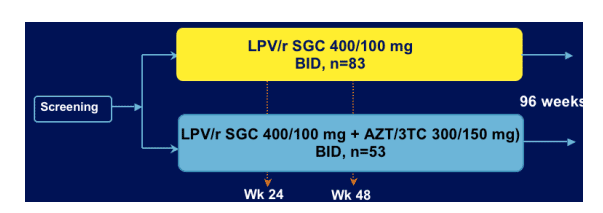
83 patients received LPV/r soft-gel capsules 400/100 mg bid and 53 patients received LPV/r soft-gel capsules 400/100 mg + AZT/3TC (300/150mg) bid.
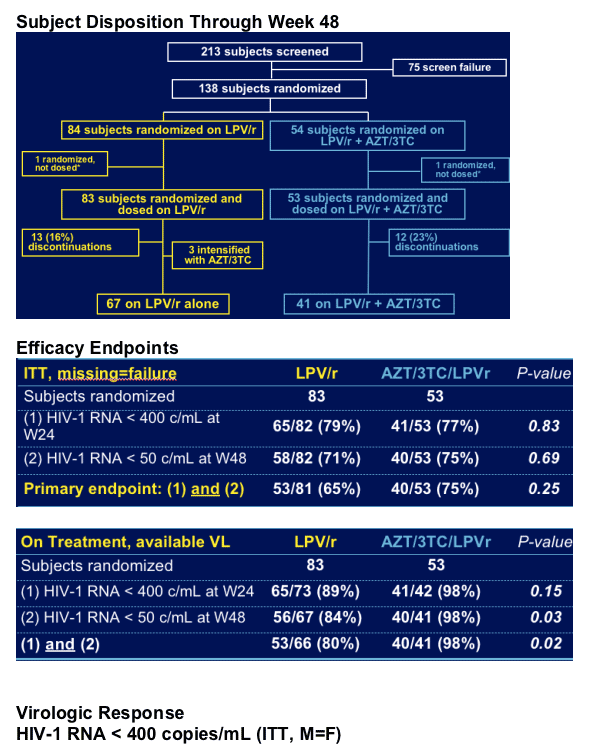
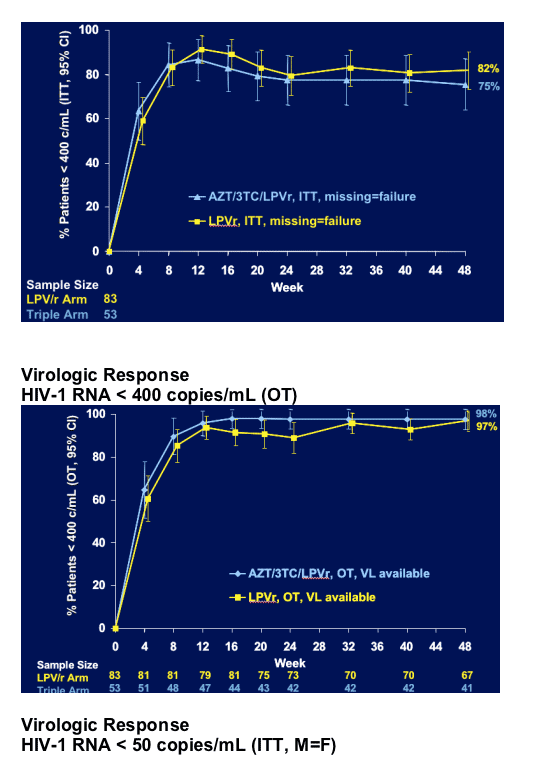
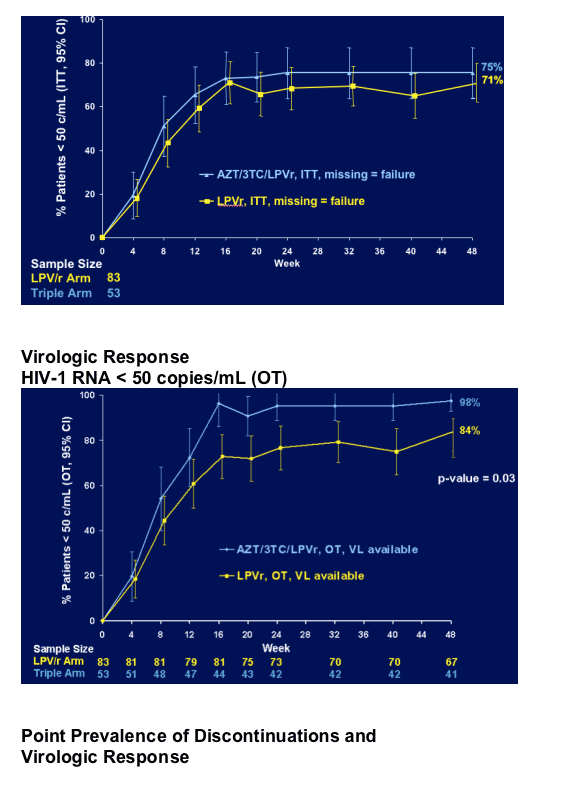
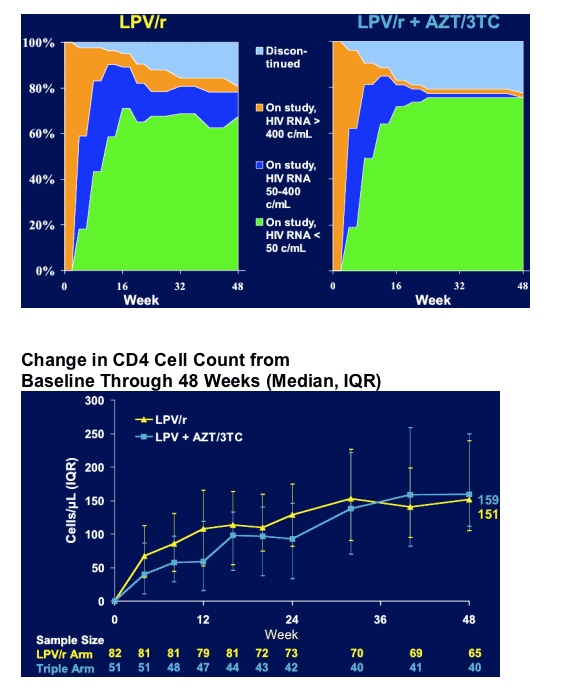
Primary efficacy analysis
Proportion of subjects with HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL at Week 24
AND < 50 copies/mL at Week 48
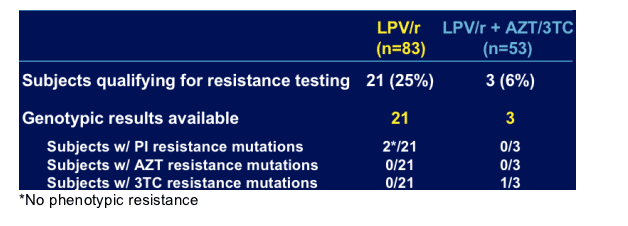
Resistance Testing
Genotypic testing performed:
-- at time of virologic failure (HIV-1 RNA > 500 c/mL after nadir
< 400 c/mL, or HIV-1 RNA > 500 c/mL at time of discontinuation
after nadir < 400 c/mL)
-- at investigator request for subject safety
2/21 on LPV/r and 0/3 on LPV/r+AZT/3TC had PI mutations. The 2 on LPV/r had no phenotypic resistance. In the LPV/r arm 0/21 had AZT or 3TC resistance mutations. In LPV/t+AZT/3TC 0/3 had AZT resistance mutations and 1/3 had 3TC mutations.
Author Conclusions
Initiating antiretroviral therapy with LPV/r monotherapy demonstrated sustained virologic efficacy
LPV/r monotherapy was associated with more episodes of viremia ( 50 < HIV-1 RNA < 400 c/mL) compared with LPV/r-based 3-drug therapy
These results are in keeping with other NRTI - sparing first line trials (Hippocampe - ANRS 121)1
However, further ongoing analysis (HIV-DNA, pharmacokinetic and adherence studies) might help defining predictive factors that identify naive patients for whom such a strategy can be proposed
These results in naive patients suggest that LPV/r monotherapy warrants further evaluation
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|