 |
 |
 |
| |
Safety and Efficacy of MARAVIROC (MVC), a Novel CCR5 Antagonist, When Used in Combination with Optimized Background Therapy (OBT) for the Treatment of Antiretroviral-Experienced Subjects Infected with Dual/Mixed-Tropic HIV-1: 24-Week Results of a Phase 2b Exploratory Trial
|
| |
| |
Reported by Jules Levin
XVI Intl AIDS Conference, Toronto, Aug 17, 2006
These are the study results reported in the poster version of the oral presentation in the Late Breaker session Thursday in Toronto. There were 18 oral talks in the Late Breaker session and each was limited to 7 minutes. This poster has more information from the study than was reported in the oral: the Secondary Efficacy Endpoints at week 24 (table 4); more details of the Clinical and Lab Adverse Events.
Howard Mayer1, Elna van der Ryst2, Michael Saag3, Bonaventura Clotet4, Gerd Fätkenheuer5, Nathan Clumeck6, Karen Turner2, and James M. Goodrich1
Pfizer Global Research and Development, 1New London, USA, and 2Sandwich, UK, 3University of Alabama at Birmingham, USA, 4University Hospital Germans Trias i Pujol, Badalona (Barcelona), Spain,
5University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany, 6St Pierre University Hospital, Brussels, Belgium
INTRODUCTION & STUDY OBJECTIVES
- MARAVIROC (MVC) is a CCR5 antagonist with potent anti-HIV-1 activity in vitro and in vivo against CCR5 (R5)- but not CXCR4 (X4)-tropic HIV-1 strains and is currently in Phase 2b/3 development in both treatment-naive and -experienced patients.1,2
- Unlike currently available therapies, which inhibit viral targets (reverse transcriptase, protease and gp41), MVC has been shown to inhibit a co-receptor target (CCR5) on the surface of host CD4+ cells in vitro. This mode of action,
which inhibits virus/cell binding, underpins MVC's activity against both wild-type HIV-1 and virus that is resistant to currently available therapies.1
- R5-tropic HIV-1 predominates early in infection with X4-tropic HIV-1 being detectable in approximately 50% of treatment-experienced patients prior to death.
- The detection of X4-tropic HIV-1 has been associated with more rapid CD4 cell depletion and progression to AIDS.3 However, it is unclear whether the emergence of X4-tropic HIV-1 is the cause or result of the more rapid CD4 decline.
- It is unclear what effect MVC will have on viral suppression when administered with optimized background therapy (OBT) to patients with non-R5-tropic HIV-1 (dual/mixed (D/M)-tropic, only X4-tropic or indeterminate HIV-1). However, there is concern that if MVC suppresses the R5-tropic HIV-1, the X4-tropic HIV-1 population could expand and result in more rapid CD4 decline and disease progression. This study evaluates the safety, efficacy and tolerability of two doses of MVC added to OBT versus placebo + OBT alone, in treatment-experienced patients with D/M-tropic HIV-1 infection.
METHODS
Study design
- A4001029 is an ongoing, 48-week, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled Phase 2b study of MVC in treatment-experienced (triple-class experience and/or dual-class-resistant HIV-1) patients with HIV-1 RNA ≥5000 copies/mL & non-R5-tropic (X4-tropic, D/M-tropic or indeterminate) HIV-1 infection.
- Patients were stratified at screening by HIV-1 RNA <100,000 versus ≥100,000 copies/mL and prior enfuvirtide use in the OBT.
- Eligible patients were randomized 1:1:1 to one of three arms:
1. OBT (comprising 3 to 6 open-label antiretroviral drugs [not counting low-dose ritonavir] of which at least one is active and no more than one is an NNRTI) and placebo
2. OBT plus MVC 150 mg QD
3. OBT plus MVC 150 mg BID.
- Patients whose OBT did not contain a protease inhibitor (PI) or the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) delavirdine, received doses of MVC 300 mg QD or BID according to their original randomization.
- Co-receptor tropism testing (using Monogram Biosciences PhenoSenseTM entry assay) was performed in all patients who met any of the criteria for treatment failure and in all patients with HIV-1 RNA ≥500 copies/mL at screening, weeks 4, 8 and every 8 weeks thereafter.
- The primary endpoint of this analysis was the change from baseline to 24 weeks in viral load for patients with D/M-tropic HIV-1 at screening, using the full analysis set (patients who were randomized and received at least one
dose of study drug).
- Secondary efficacy endpoints included: proportion of patients who achieved HIV-1 RNA <400 copies/mL, <50 copies/mL; decrease from baseline of at least 0.5 or 1.0 log10 copies/mL; change in CD4 cell counts; and HIV-1 tropism at baseline and at the time of failure.
- Treatment failure was defined as meeting any one of the following virologic endpoints.
- An increase to at least three times the baseline (mean of all three values before start of dosing) plasma HIV-1 RNA level at the week 2 visit or thereafter (confirmed by a second measurement taken no more than 14 days after the
first measurement).
- HIV-1 RNA <0.5 log10 decrease from baseline (mean of all three values before start of dosing) on two consecutive measurements starting at Week 8 (second measurement taken no more than 14 days after the first measurement).
- HIV-1 RNA <1.0 log10 decrease from baseline (mean of all three values before start of dosing) on two consecutive measurements starting at Week 8 (second measurement taken no more than 14 days after the first measurement),
in a patient who had previously achieved a ≥2.0 log10 decrease from baseline.
- An increase in HIV-1 RNA to ≥5,000 copies/mL, on two consecutive measurements taken no more than 14 days apart, in patients previously confirmed to have undetectable levels of <400 copies/mL on two consecutive visits.
Safety analysis
- Safety was assessed by spontaneous reports, physical examination and laboratory test results in all patients who received at least one dose of study medication.
Statistical analysis
- Efficacy data were analyzed using the full analysis set which included all randomized patients who had received at least one dose of the study drug. Patients treated but with no on-treatment assessment were imputed as zero for the primary efficacy analysis.
- 97.5% confidence intervals (adjusted for multiple comparisons) were calculated for the difference between placebo + OBT and the MVC + OBT arms.
RESULTS
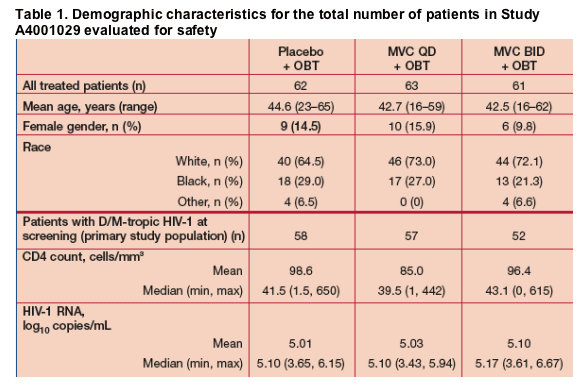
One hundred and ninety patients enrolled in the study and underwent randomization, with 186 patients receiving at least one dose of study drug. Demographic details of all 186 patients who underwent randomization and
treatment are shown in Table 1.
- 167 patients had D/M-tropic HIV-1 at screening and represented the primary study population. This study population was very advanced, with an overall median baseline CD4 cell count of <50 cell/mm3 and a baseline viral load (mean of pre-dose measurements) of >5 log10 HIV-1 RNA copies/mL for all three treatment arms.
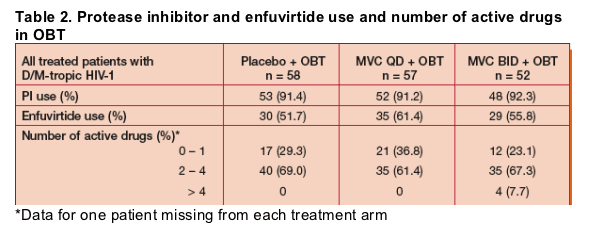
- More than 91% and 52% of patients in each arm of the study received a PI or enfuvirtide respectively.
- The number of active drugs in OBT was slightly greater in the MVC BID arm than in the other 2 arms. All patients who had more than 4 active drugs were in the MVC BID arm (Table 2).
Efficacy Data
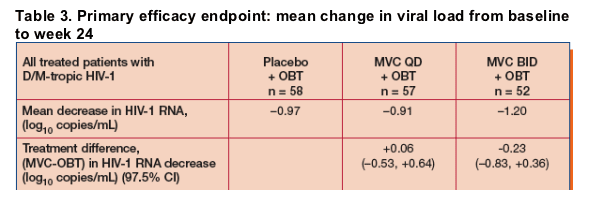
- The primary efficacy endpoint (mean change in viral load from baseline to week 24 in all three treatment arms) and the difference in viral load reduction between each of the MVC + OBT treatment arms and the placebo + OBT treatment arm is shown in Table 3.
- Reduction in viral load from baseline to week 24 was similar for the MVC QD + OBT (-0.91 log10) and placebo + OBT treatment arms (-0.97 log10) and slightly but not statistically greater for the MVC BID arm (-1.20 log10).
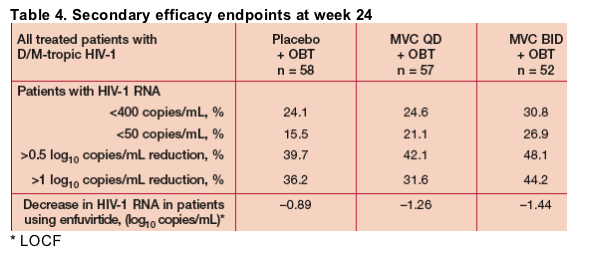
- The secondary efficacy endpoints are shown in Table 4. All patients who discontinued prior to week 24 were included as non-responders.
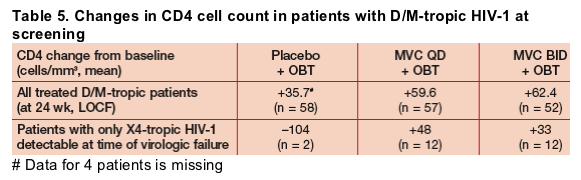
- Mean change from baseline to week 24 in CD4 cell count was similar between both MVC arms (QD +59.6 cells/mm3, BID +62.4 cells/mm3) and substantially higher than that observed in the placebo + OBT arm (+35.7 cells/mm3) as shown
in Table 5.
- These differences in CD4 count were not associated with changes in CD4 cell percentage.
- Patients receiving MVC + OBT were more likely to fail with X4-tropic HIV-1 than those receiving placebo + OBT. However, patients treated with MVC + OBT who had X4-tropic HIV-1 at treatment failure had similar increases in CD4 count to the overall MVC-treated population.
Clinical and Laboratory Adverse Events (AEs)
- In general, MVC was well tolerated with few differences in types, frequency or severity of AEs amongst all three treatment arms. Incidence of Grade 3 or 4 AEs was also similar across the three treatment arms.
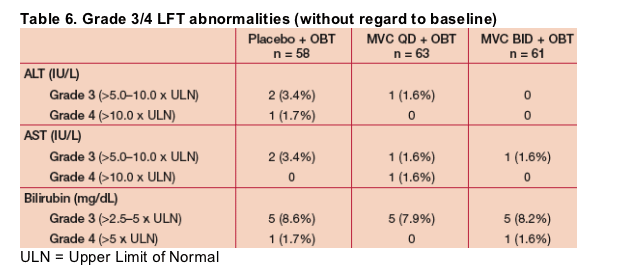
- Hepatotoxicity was not observed and ALT, AST and bilirubin elevations were similar between the MVC and placebo arms as shown in Table 6.
- No cases of lymphoma or adenocarcinoma were reported in any patients in this study through 24 weeks.
- There were a total of 13 AIDS-defining Category C infections during the 24-week observation period:
- Placebo + OBT arm (n=3): one case of progressive mulitifocal leukoencephalopathy, one recurrent pneumonia, and one esophageal candidiasis.
- MVC QD + OBT arm (n=7): three cases of pneumocystis pneumonia, one herpes simplex virus infection, one cytomegalovirus retinitis, and one subject with both disseminated histoplasmosis and Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare.
- MVC BID + OBT arm (n=3): two cases of esophageal candidiasis and one pneumocystis pneumonia.
- There were a total of seven deaths that occurred either on active treatment or post-treatment in the trial (three in the placebo + OBT treatment arm, two in the MVC QD + OBT treatment arm, two in the MVC BID + OBT treatment arm). None of these deaths were considered by the investigator to be related to the study drug.
Author Summary & Conclusion
Over 24 weeks, in treatment-experienced patients with D/M-tropic HIV-1 and advanced disease:
- MARAVIROC + OBT was generally well tolerated
- No cases of hepatotoxicity, lymphoma or adenocarcinoma
- MARAVIROC + OBT did not demonstrate superior reductions in HIV-1 RNA compared with placebo + OBT
- MARAVIROC + OBT was associated with greater increases in CD4 cell count than placebo + OBT
- Patients receiving MARAVIROC + OBT were more likely to fail with X4-tropic HIV-1 than those receiving placebo + OBT.
- However, patients treated with MVC + OBT who had X4-tropic HIV-1 at treatment failure had similar increases in CD4 cell count to the overall MARAVIROC-treated population
References
1. Dorr P et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005;49:4721-32.
2. Fätkenheuer G et al. Nat Med 2005;11:1170-2.
3 Schuitemaker H et al. J Virol 1992;66:1354-1360
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|