 |
 |
 |
| |
New Fusion Inhibitor Peptides, TRI-999 and TRI-1144, are Potent Inhibitors of Enfuvirtide and T-1249 Resistant Isolates
|
| |
| |
Reported by Jules Levin
XVI IAC Toronto, Aug 2006
D.K. Davison1, R.J. Medinas1, S.M. Mosier1, T.S. Bowling1,
M.K. Delmedico1, J.J. Dwyer1, N. Cammack2, M.L. Greenberg1
1Trimeris, Inc., Morrisville, NC, USA; 2Roche, Palo Alto, CA, USA
poster THPE0021
Author Conclusions:
Mutations seen in ENF and T-1249 in vitro selections were similar to those observed in clinical trials.
TRI-999 and TRI-1144 retained activity against ENF- and T-1249-resistant isolates.
Those results, combined with:
-- a. an inability to obtain virus break-through in concentrations of TRI-999 and TRI-1144 over 30-fold lower than with ENF or T-1249 along with
-- b. higher numbers of mutations required to generate resistance suggest these next generation FIs have enhanced genetic barriers to resistance.
The basis for the enhancements in the resistance profile and genetic barrier of these peptides is under investigation.
Introduction
Enfuvirtide (ENF) is a 36 amino acid peptide derived from the HR2 region of HIV-1 LAI (Figure 1) and is the first approved fusion inhibitor (FI) for the treatment of HIV. Clinical trials of ENF revealed primary resistance mutations occurring within gp41 positions 36-45 [1] and site directed mutagenesis confirmed many of their effects [2]. T-1249, an FI previously in development, is a 39 amino acid peptide derived from the HR2 regions of HIV-1, HIV-2 and SIV (Figure 1). T-1249 demonstrated activity against ENF-resistant viruses in vitro and in vivo [3,5]. T-1249 also selects for mutations within positions 36-45 and outside of this region [4-6]. Two new investigational fusion inhibitors (FIs), TRI-999 and TRI-1144, display potent activity against ENF- and T-1249-resistant isolates selected in vitro [7]. TRI-999 and TRI-1144 were designed from a more N-terminal region of HR2 than ENF (Figure 1). TRI-999 consists of an optimized wild-type HR2 sequence plus a linker-fatty acid attached to an internal lysine. TRI-1144 contains helix-stabilizing motifs such as salt bridges and alanine substitutions, along a similar region of HR2.
Methods
Eight HIV-1 isolates, five baseline virus isolates from an ENF clinical trial (030, 042, 060, 093 and 098) and three additional ENF na•ve isolates (DH012, RF and A018), were used to infect CEM4, MT2 or MT4 cells and cultured with increasing
concentrations of ENF or T-1249 to select for resistance. When these in vitro selections reached 20 or 50_g/ml, virus stocks were expanded in the presence of 20 or 50_g/ml of peptide and peptide-free virus stocks were harvested. Each stock was characterized for gp41 genotypic changes by dideoxy sequencing
chemistries using a Beckman Coulter CEQ 20000XL system and DNA-Star software as described [1]. Phenotypic susceptibility to the selecting peptides and to the new FI peptides, TRI-999 and TRI-1144, was determined by MAGI/cMAGI infectivity assay [8].
RESULTS
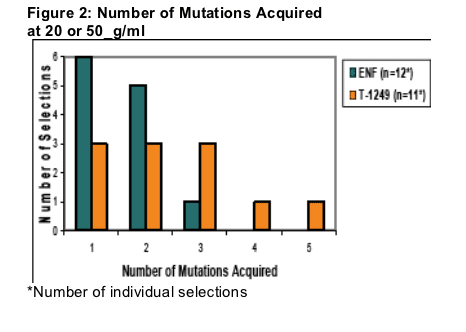
Multiple in vitro selections were conducted with several virus isolates resulting in a total of 12 ENF in vitro selections and 11 T-1249 in vitro selections. The ENF selections were in culture an average of 36 days to reach 20 or 50_g/ml with a range of 20-65 days. In contrast, the T-1249 selections were in culture an average of 63 days to reach 20 or 50_g/ml with a range of 33-101 days. The gp41 ectodomain of the virus isolates was sequenced to identify amino acid changes occurring in this region during selection. Eleven of 12 ENF selections acquired 1 or 2 mutations with an average of 1.6 mutations noted for all, while T-1249 selections acquired 1-5 mutations with an average of 2.5 mutations (Figure 2).
ENF Selections
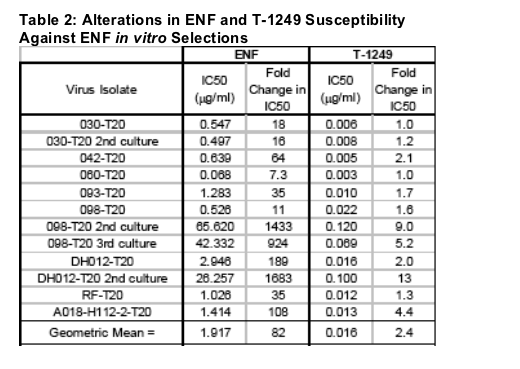
ENF selections predominately resulted in mutations within HR1 at positions 36-45 (Table 1). Changes were also noted outside of this region, perhaps indicating secondary or compensatory mutations. Each selected isolate was tested against ENF and T-1249 to assess alterations in peptide susceptibility (Table 2). ENF selections resulted in fold changes to ENF ranging from 7 to 1683 with a geometric mean fold change of 82. Of note, two independent selections with the 030 virus led to similar mutations yielding nearly identical fold changes in ENF susceptibility. In contrast, three selections with the 098 isolate contained different
mutations and fold changes to ENF that ranged from 11 to -1400. A similar spread in fold changes to ENF selection resulting from different mutations arising during selection was seen with two ENF selections conducted with the DH012 virus.
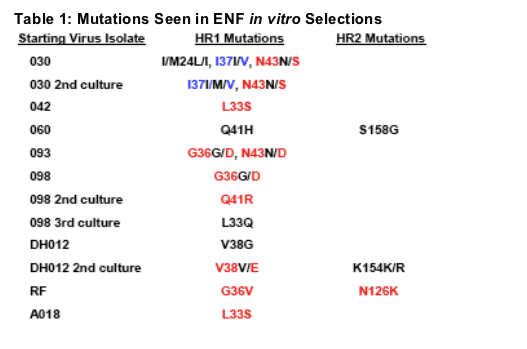
The mutations shown here in RED have been confirmed to impact ENF susceptibility by >5-fold using site-directed mutagenesis (SDM). The mutations shown here in BLUE impact ENF susceptibility by <5-fold. Mutations shown in BLACK have not been tested by SDM.
T-1249 Selections
While ENF selected isolates lost substantial sensitivity to ENF they remained relatively sensitive to T-1249 with a geometric mean fold change of 2.4. However, several exceptions were noted. A Q41R mutation arising in an 098 selection and a DH012 selection resulting in a V38V/E mutation led to 9- and 13-fold decreases in T-1249 susceptibility respectively (Tables 1 and 2). The Q41R and V38E mutations also arose during selection with T-1249 in vitro (Table 3), and the V38E mutation has been seen in patients participating in T-1249 clinical trials [4,5]. Additional mutations seen in T-1249 in vitro selections are listed in Table 3.
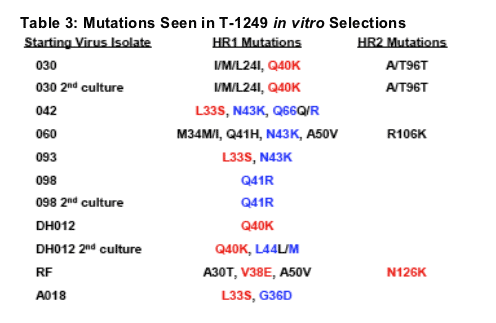
The mutations shown here in RED have been confirmed to impact ENF susceptibility by >5-fold using site-directed mutagenesis (SDM). The mutations shown here in BLUE impact ENF susceptibility by <5-fold. Mutations shown in BLACK have not been tested by SDM.
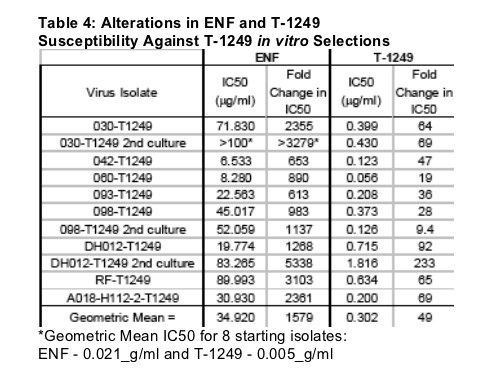
Most mutations arising during T-1249 selection occurred in HR1 within positions 36-45 but additional mutations outside of this region were also observed (Table 3). T-1249 selection resulted in a dramatic decrease in ENF sensitivity with a geometric mean fold change >1500 (Table 4). The overall loss of T-1249 activity was 49-fold and ranged from 9 to 233. Thus, during these selections isolates highly resistant to ENF and T-1249 were generated. We assessed the activity of TRI-999 and TRI-1144, two newer experimental fusion inhibitor peptides, against all ENF and T-1249 resistant isolates generated through in vitro selections (Tables 5 and 6).
TRI-999 and TRI-1144 Activity Against ENF and
T-1249 Resistant Isolates
Both TRI-999 and TRI-1144 retained substantial activity against ENF-resistant isolates (Table 5) with geometric mean fold changes of ~1 for the entire panel of ENF selected isolates.
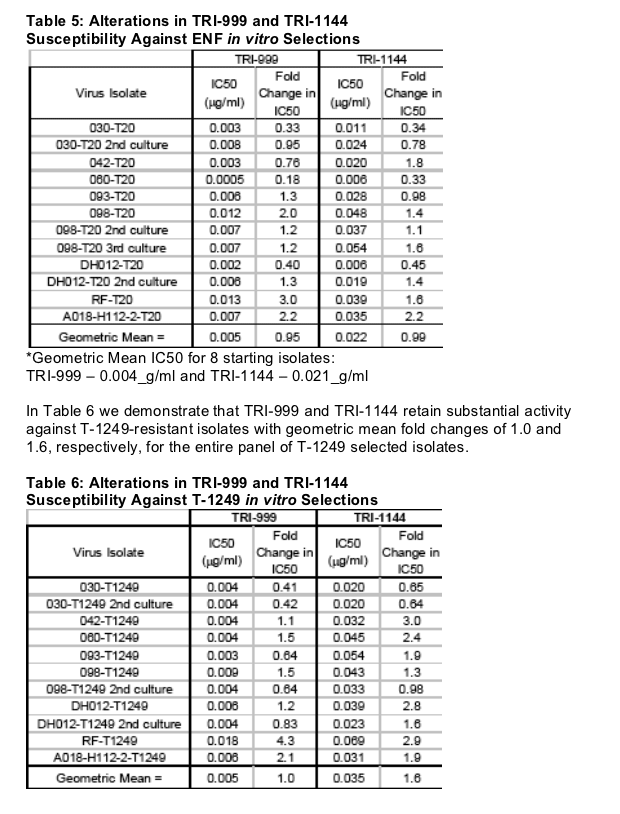
*Geometric Mean IC50 for 8 starting isolates:
TRI-999 - 0.004_g/ml and TRI-1144 - 0.021_g/ml
TRI-999 and TRI-1144 Selections
TRI-999 and TRI-1144 in vitro selections were started with 3 virus isolates (IIIB, 030 and 098). Selections with TRI-999 reached 0.01-0.05_g/ml after 71-76 days yielding 0-3 mutations with a geometric mean fold change <2. Selections with TRI-1144 reached 0.1-0.6_g/ml after 72-93 days yielding 1-2 mutations with a geometric mean fold change <5.
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|