 |
 |
 |
| |
Determination of Body Composition Changes by Total Body Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry after 48 Weeks of Treatment with Once-Daily Fosamprenavir (FPV) Boosted with Two Different Doses of Ritonavir(r) plus Abacavir(ABC)/ Lamivudine(3TC): COL100758
|
| |
| |
Reported by Jules Levin
4th IAS Conference, July 22-25, 2007, Sydney, Australia
D. Wohl1, T. Lancaster2, E. DeJesus3, L. Sloan4, M. Sension5, Q. Liao2, and C. Hicks6
1UNC Chapel Hill, NC, 2GlaxoSmithKline, NC; 3Orlando Immunology Ctr, FL; 4N Texas Inf Disease Consultants, TX; 5Comprehensive Care Ctr, FL; and 6Duke Univ, NC
Using whole body dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), we sought to determine the differential affects of co-administration of fosamprenavir with
200 mg vs. 100 mg of ritonavir on body fat composition and bone mineral
density in antiretroviral treatment-naive men and women.
AUTHOR DISCUSSION
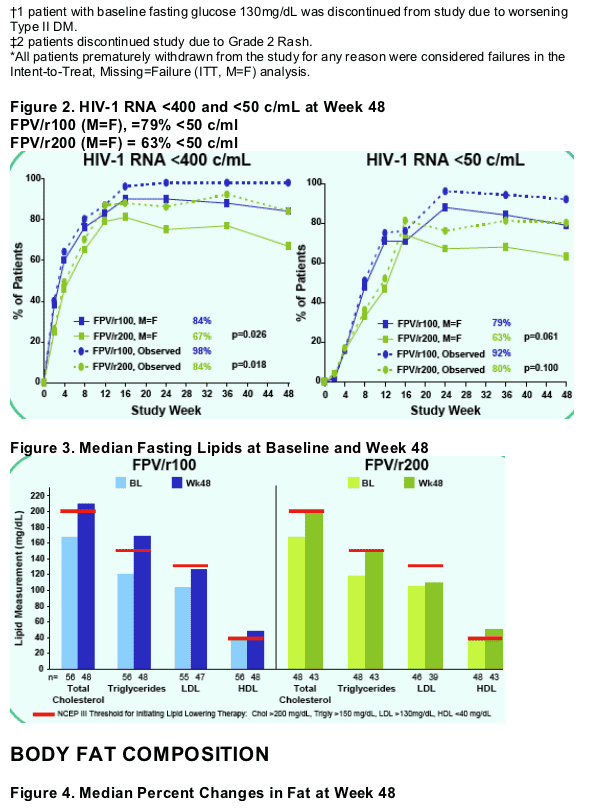
Although trunk fat increases >20% were more common with FPV/r200, the
difference was not statistically significant.
No patient with available paired baseline and week 48 DXA data had simultaneous increases >20% in trunk fat and either combined arm or leg fat
decreases >20%.
Fat changes by DXA reported in this study are similar to 48 week data previously reported for the protease inhibitor atazanavir boosted with ritonavir 100 mg daily.4
Changes in glucose and insulin were unremarkable and similar.
AUTHOR CONCLUSION
After 48 weeks of treatment with once-daily FPV/r + ABC/3TC, median limb and trunk fat depots increased similarly when FPV was co-administered with either 100 mg or 200 mg of ritonavir.
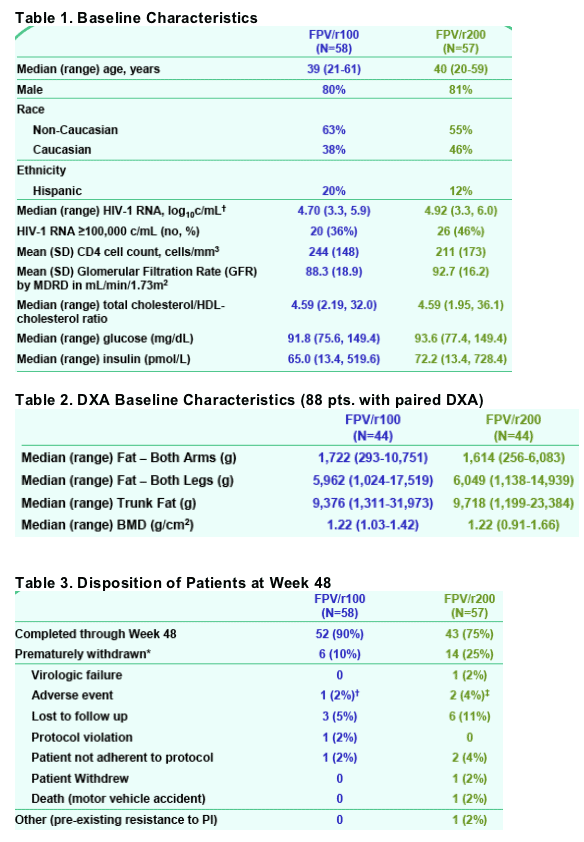
Clinically relevant changes in fat (>20% loss of extremity fat or >20% increase in trunk fat) tended to occur less frequently in patients assigned to FPV/r100.
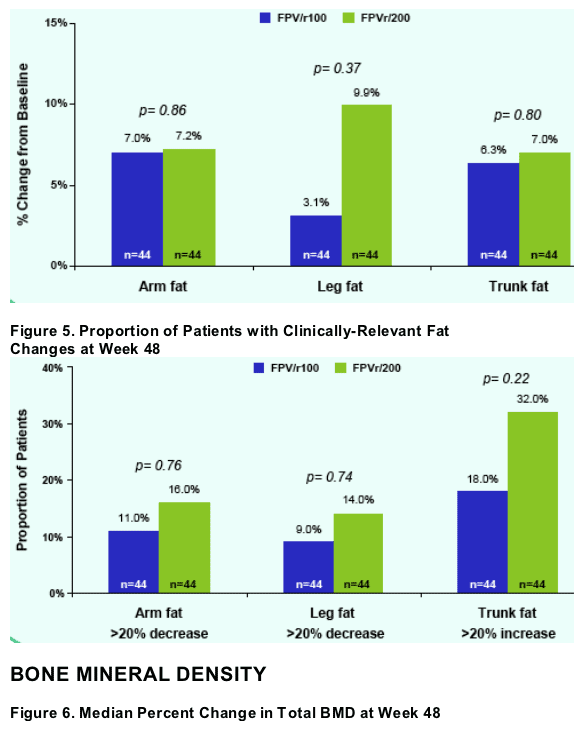
Total BMD change was small and not significantly different between study groups.
Differences in efficacy at week 48 favored FPV/r100.
Additional metabolic and body composition data through 96 weeks may provide further insight into the metabolic effects of the two doses of FPV/r investigated in this study.
Study Regimens
Participants were randomized to receive 1400 mg of fosamprenavir once-daily along with 100 mg of ritonavir (FPV/r100) versus 200 mg of ritonavir (FPV/r200). All received fixed-dose abacavir/lamivudine (ABC/3TC), and 7 patients presumed hypersensitive to ABC were allowed to remain on study upon switching to ZDV/3TC.
Body Fat Composition
Whole body DXA scans (using Hologic and Lunar Scanners) were obtained
at study entry and week 48 for 48 patients. 80% of patients were evaluated
with Hologic scanners.
Changes in regional fat including combined upper limbs, combined lower
limbs and trunk were compared between study groups. The proportion of
patients in each group with >20% (combined) arm fat decrease, >20%
(combined) leg fat decrease or >20% trunk fat increase were compared.
Bone Density
Bone mineral density (BMD) was evaluated at study entry and week 48 by
whole body DXA scanning. Changes in total body BMD were compared
between study groups.
Statistical Methods
Percent changes in arm fat, leg fat, trunk fat, and total body BMD between
the 2 treatment arms were compared using Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
Comparisons of proportion of patients with clinically relevant fat changes
were made using Fisher exact test.
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|