 |
 |
 |
| |
Pharmasset Presents Results of 4-Week Combination Study of R7128 for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C
|
| |
| |
- 85% of patients achieve undetectable HCV RNA levels following 4 weeks of treatment with R7128 1500mg BID with Pegasys(R) plus Copegus(R) -
- Safety and tolerability comparable to placebo administered with Pegasys plus Copegus -
PRINCETON, N.J. and MILAN, Italy, April 25, 2008 /PRNewswire-FirstCall via COMTEX News Network/ -- Pharmasset, Inc. (Nasdaq: VRUS) announces the results of a 4-week Phase 1 clinical trial evaluating two oral dose levels of R7128 in combination with Pegasys (pegylated interferon) plus Copegus (ribavirin) in 50 treatment-naive patients chronically infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1. R7128, a prodrug of PSI-6130, is a nucleoside analogue polymerase inhibitor of HCV that is being developed through Pharmasset's collaboration with Roche. The results of this study were presented today at the 43rd Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) being held from April 23-27, 2008 in Milan, Italy.
In this study, R7128 demonstrated potent short-term antiviral activity and was generally safe and well tolerated. Eighty-five percent (85%) of patients receiving R7128 1500mg twice-daily (BID) with Pegasys plus Copegus for 4 weeks achieved undetectable HCV RNA levels with safety and tolerability comparable to placebo with Pegasys plus Copegus.
Dr. John McHutchison, professor of medicine at Duke University Medical Center and a clinical investigator for this study, stated, "R7128, in combination with Pegasys plus Copegus, has demonstrated Rapid Virologic Response (RVR) percentages in a 4-week study that are similar to HCV protease inhibitors and has an encouraging short-term clinical safety profile. Longer-term studies of R7128 with Pegasys plus Copegus are needed to provide additional information about its potential to improve sustained virologic response (SVR) rates for HCV patients."
R7128 4-week Combination Study Overview
The 4-week Phase 1 combination clinical trial was a multiple center, observer-blinded, randomized and placebo-controlled study that was conducted in 50 treatment-naive patients chronically infected with HCV genotype 1. The primary objective was to assess the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of R7128 in combination with Pegasys plus Copegus. The secondary objective was to evaluate the change in HCV RNA after 4 weeks of treatment.
The study investigated two oral dose levels of R7128, 500mg and 1500mg, each administered twice-daily (BID) with once-weekly injections of Pegasys plus Copegus BID. Each cohort of 25 patients was comprised of 20 patients receiving R7128 and 5 patients receiving placebo with Pegasys plus Copegus.
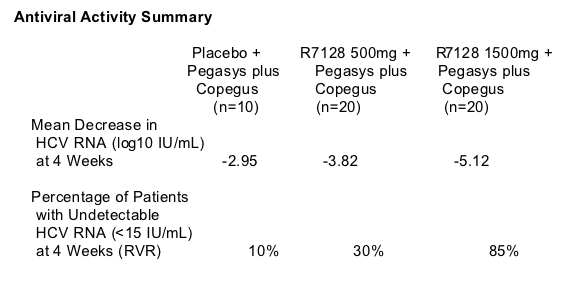
Potent antiviral activity was demonstrated following 4 weeks of treatment with R7128 1500mg BID with Pegasys plus Copegus. These patients achieved a mean 5.12 log10 IU/mL decrease in HCV RNA and 85% (17 of 20) had undetectable levels of HCV RNA (<15 IU/mL), or RVR. Following 4 weeks of treatment with R7128 500mg BID with Pegasys plus Copegus, patients achieved a mean 3.82 log10 IU/mL decrease in HCV RNA and 30% (6 of 20) had RVR. Following 4 weeks of treatment with placebo with Pegasys plus Copegus, patients achieved a mean 2.95 log10 IU/mL decrease in HCV RNA and 10% (1 of 10) had RVR. The baseline HCV RNA levels for all patients in the study were greater than 6.3 log10 IU/mL and were similar across all study groups.
Safety Summary
Safety and tolerability for the 4-week treatment period were similar for R7128 with Pegasys plus Copegus compared to placebo with Pegasys plus Copegus. There were no serious adverse events reported during the 4-week treatment period, and most of the adverse events reported were of mild to moderate intensity. The most common adverse events, reported in 15% or greater of patients in any treatment group during the 4-week treatment period, were headache, injection site reaction, myalgia, fatigue, chills, rash, nausea, diarrhea, arthralgia, pyrexia, dizziness, dyspepsia and pruritis. The frequency and severity of these adverse events, as well as any general body system observations, were generally similar to clinical experience with the standard of care for HCV, pegylated interferon plus ribavirin.
Grade 3/4 neutropenia was observed in 30% of the placebo patients and in 10% to 15% of the R7128 patients in each active dosing cohort. Grade 3 changes in hemoglobin were observed in 10% of the placebo patients and in 15% of the R7128 patients. There were no clinically significant changes in other hepatic, renal, or other safety laboratory parameters, vital signs, or electrocardiograms.
Overall, there was no clinical evidence of any major organ toxicities related to R7128. One patient in the active treatment group discontinued the study during the 4 week treatment period due to lower-gastrointestinal adverse events. At the time of study discontinuation, this patient had undetectable HCV RNA. R7128 was generally safe and well-tolerated when administered for 4 weeks in combination with Pegasus plus Copegus in patients with HCV genotype 1.
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|