 |
 |
 |
| |
SOFOSBUVIR PLUS VELPATASVIR FOR CHRONIC HCV GENOTYPE
1, 2, 3, AND 4 INFECTION
|
| |
| |
Reported by Jules Levin
EASL 2016 April 14-17 Barcelona
Hussien Ahmed1,2,3, Arwa Mohamed1,2, Attia Attia1,4, Ahmed Negida1,2,3 *
[1] Medical Research Group of Egypt; [2] Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University; [3] Student Research Unit, Zagazig University; [4] Faculty of Medicine, Al Azhar University.
* Correspondence to Dr.Ahmed Negida; Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt; Head of Scientific Committee of the Student Research Unit, Zagazig University, Egypt; and Chairman of Medical Research Group of Egypt; emails: ahmed01251@medicine.zu.edu.eg and ahmed-negida@sru-zu.org ; Tel: +201125549087
Background
The newly FDA approved NS5B nucleotide inhibitor sofosbuvir is effective against all HCV genotypes, with a better safety profile and lower risk of development of resistance. The active form of sofosbuvir mimics the physiological nucleotide and competitively blocks the NS5B polymerase, thereby inhibiting the HCV-RNA synthesis via RNA chain termination. Velpatasvir (formerly known as GS-5816, Gilead Sciences) is another inhibitor of the HCV NS5A protein with antiviral action against all HCV genotypes. Recently, multiple studies have evaluated the efficacy of the combination Sofosbuvir plus Velpatasvir for the treatment of different HCV genotypes.
Objectives
We performed this systematic review and meta-analysis to precisely estimate the sustained virologic response (SVR) achieved by Sofosbuvir plus Velpatasvir for chronic HCV genotype 1, 2, 3, and 4 Infection.
Materials and Methods
A computer literature search of PubMed, SCOPUS, web of knowledge, and Cochrane CENTRAL has been conducted using relevant keywords. Studies were screened for eligibility and data were extracted to an online data extraction form.
Sustained Virologic Response rates were pooled in a fixed effect model meta-analysis using Mantel-Haenzel method. Heterogeneity was assessed by visual inspection of the forest plots and measured by Chi-square and I-square tests. Statistical analysis was performed by OpenMeta[Analyst] software (by Center of Evidence Based Medicine http://www.cebm.brown.edu/open_meta/).
Results
Five articles (6 clinical trials; n=2407 patients) were pooled in the final analysis. For non-cirrhotic patients who received 400 mg Sofosbuvir plus 100 mg Velpatasvir, SVR was 97.1% with 95% CI [92.7% to 101.5%]. For cirrhotic patients who received 400 mg Sofosbuvir plus 100 mg Velpatasvir, SVR were as follows (for genotype 1a, SVR=97.8% with 95% CI [96.1% to 99.4%]; for genotype 1b, SVR=99% with 95% CI [97.4% to 100%]; for genotype 2, SVR=99.4% with 95% CI [98.4% to 100%]; for genotype 3, SVR=83% with 95% CI [66.1% to 100%]; and for genotype 4, SVR=99.7% with 95% CI [98.9% to 100%]). When Ribavirin was added to the treatment regimen, patients with genotype 1a showed less SVR (95.3% vs. 97.8%) while patients with genotype 3 achieved better SVR than without Ribavirin (95% vs. 83.1%); see figure 1 and figure 2.
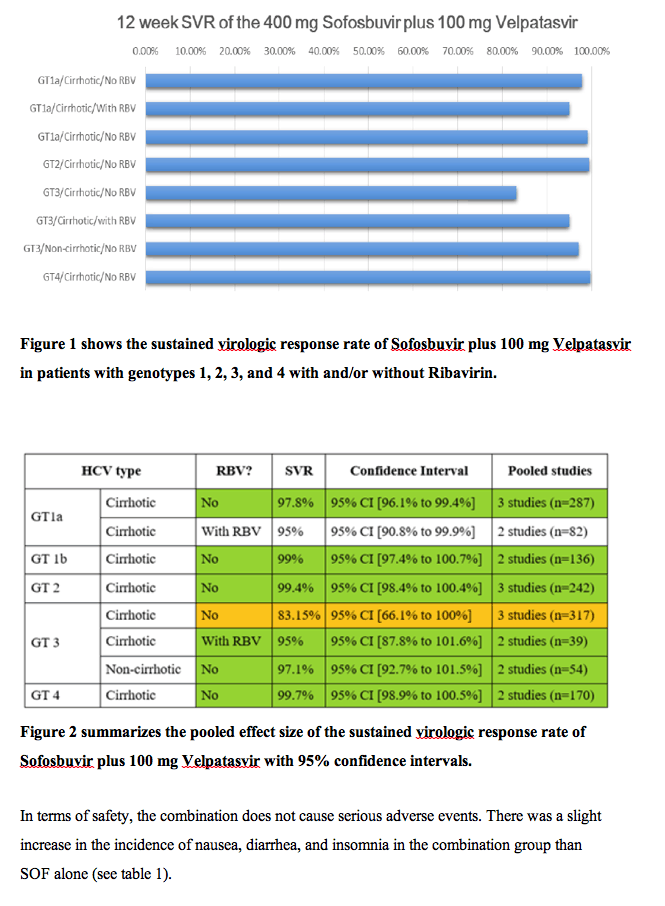
Conclusion
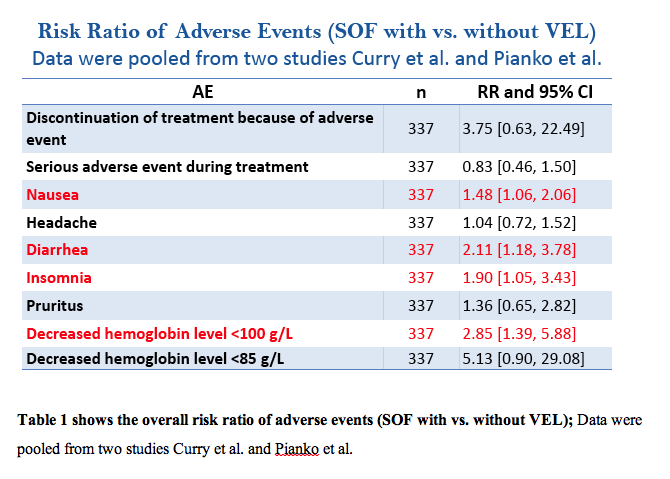
The addition of 100 mg Velpatasvir to the 400 mg Sofosbuvir achieved sustained virologic response rates ≥ 95% for cirrhotic patients with genotype 1, 2, and 4 HCV infection. But for genotype 3, the addition of Ribavirin is recommended to achieve 95% SVR. This combination (VEL/SOF) was also effective in non-cirrhotic patients with Genotype 3. The combination was safe and tolerable with slight increase in the incidence of nausea, diarrhea, and insomnia in the combination group than SOF alone.
Conflict of interest: None to declare
References
[1] Everson GT, Towner WJ, Davis MN, Wyles DL, Nahass RG, Thuluvath PJ, et al. Sofosbuvir With Velpatasvir in Treatment-Naive Noncirrhotic Patients With Genotype 1 to 6 Hepatitis C Virus Infection: A Randomized Trial. Ann Intern Med [Internet]. 2015 Dec 1 [cited 2015 Dec 9];163(11):818-26. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26551051
[2] Pianko S, Flamm SL, Shiffman ML, Kumar S, Strasser SI, Dore GJ, et al. Sofosbuvir Plus Velpatasvir Combination Therapy for Treatment-Experienced Patients With Genotype 1 or 3
Hepatitis C Virus Infection: A Randomized Trial. Ann Intern Med [Internet]. 2015 Nov 10 [cited 2015 Nov 23];163(11):809-17. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26551263
[3] Curry MP, O'Leary JG, Bzowej N, Muir AJ, Korenblat KM, Fenkel JM, et al. Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir for HCV in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis. N Engl J Med [Internet]. 2015 Nov 16 [cited 2015 Nov 18];373(27):2618-28. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26569658
[4] Feld JJ, Jacobson IM, Hézode C, Asselah T, Ruane PJ, Gruener N, et al. Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir for HCV Genotype 1, 2, 4, 5, and 6 Infection. N Engl J Med [Internet]. 2015 Nov 16 [cited 2015 Dec 1];373(27):2599-607. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26571066
[5] Foster GR, Afdhal N, Roberts SK, Bräu N, Gane EJ, Pianko S, et al. Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir for HCV Genotype 2 and 3 Infection. N Engl J Med [Internet]. 2015 Nov 17 [cited 2015 Dec 8];373(27):2608-17. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26575258
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|