 |
 |
 |
| |
Lower lipid levels in antiretroviral (ARV)-naive patients receiving the investigational NNRTI TMC278 versus efavirenz (EFV)
|
| |
| |
Reported by Jules Levin
11th European AIDS Conference, Oct 24-27, 2007, Madrid, Spain
A Pozniak,1 Y Yazdanpanah,2 P Shalit,3 S Vanveggel,4 M Peeters,4 M Stevens,4 P Williams,4 B Woodfall,4 K Boven5
1Chelsea and Westminster NHS Foundation Trust and PKR/SSR, London, UK; 2H˘pital Gustave Dron, Tourcoing, France;
3Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, WA, USA; 4Tibotec BVBA, Mechelen, Belgium, 5Tibotec Inc., Yardley, PA, USA
Abstract
Aims: TMC278, a next-generation NNRTI, has demonstrated potent and sustained efficacy in ARV-naive patients in an ongoing, Phase IIb, randomised, dose-finding study (TMC278-C204) (Pozniak et al. CROI 2007). Lipid parameters (per protocol, in fasted conditions) were evaluated and compared following TMC278 or EFV administration in TMC278-C204.
Methods: Patients received blinded TMC278 (25mg, 75mg or 150mg qd) or open-label, active control EFV 600mg qd and AZT/3TC or TDF/FTC. Lipid parameters were assessed over 48 weeks in the intent-to-treat (ITT) primary analysis.
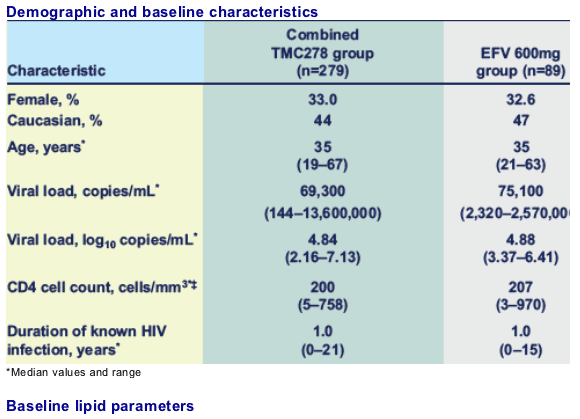
Results: 279 patients were randomised to TMC278 and 89 to EFV (33% female; median age 35 years). Seventy-six per cent of patients used AZT/3TC and 24% used TDF/FTC (proportions similar in the TMC278 and EFV groups). No substantial differences in changes in lipid parameters were observed between the TMC278 dose groups.
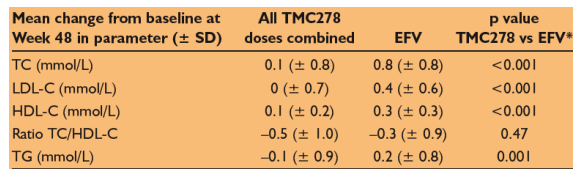
*Non-parametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test
TC = total cholesterol; LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; HDL-C =
high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; TG = triglyceride
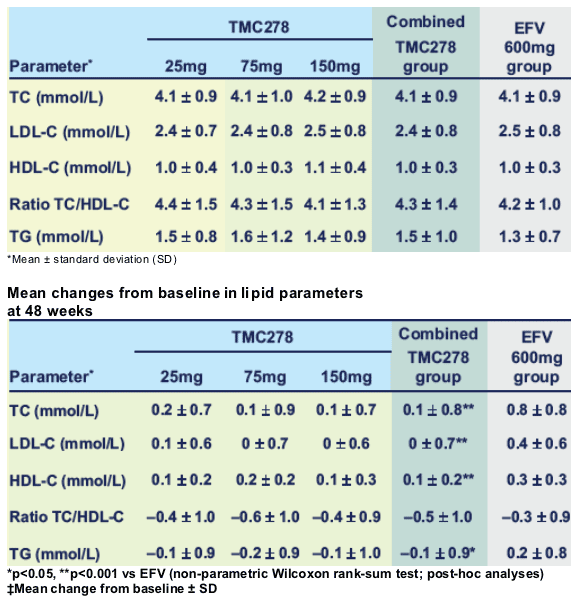
Mean changes from baseline in TC, LDL-C and TG were significantly lower in the combined TMC278 group than in the EFV group (Table). Increases in HDL-C occurred in both groups, albeit to a significantly lesser extent with TMC278 than with EFV; there was no difference in the change in ratio of TC/HDL-C. There were low incidences of grade 3/4 elevations in TC (0% vs 1.1%, respectively) and LDL-C (1.1% vs 0%).
Conclusions: Up to Week 48, the effect of TMC278 on lipid parameters was limited and compared favourably to EFV in ARV-naive patients.
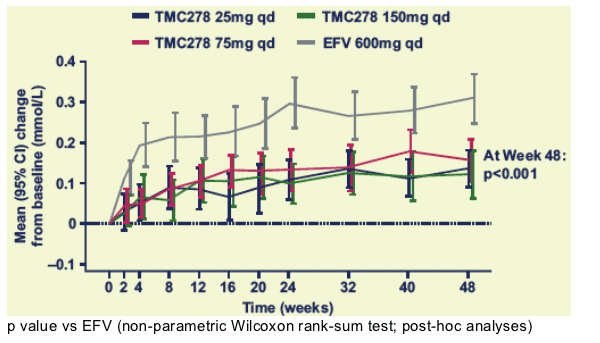
Mean changes in total cholesterol over time
There was a clear increase from baseline in TC for the EFV group, but a minimal increase for the TMC278 dose groups
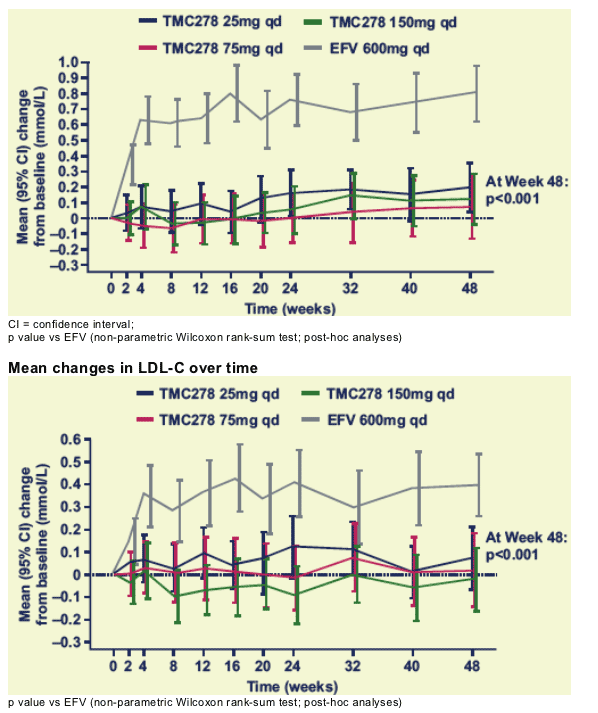
Mean changes in HDL-C over time
HDL-C levels increased over time in all groups, but more so in the EFV group than in the TMC278 dose groups
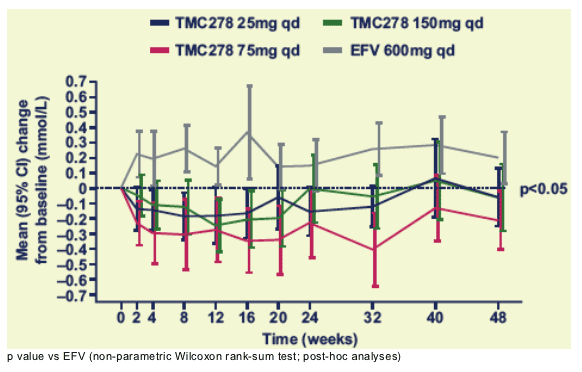
Mean changes in TC/HDL-C ratio over time
The TC/HDL-C ratio declined from baseline in all groups; the decline was not significantly different among groups
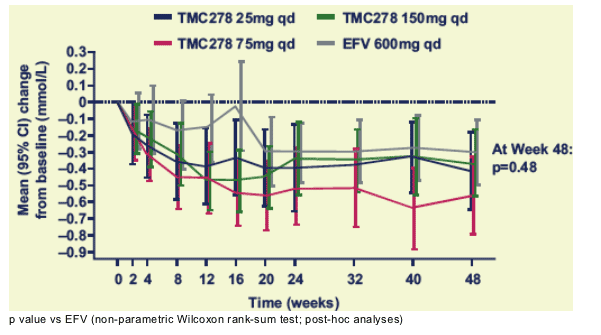
Mean changes in triglycerides over time
There was a small increase from baseline in triglycerides for the EFV group, but not for the TMC278 dose groups
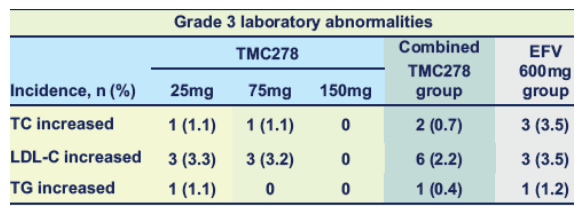
Grade 3 and 4 elevations in lipid parameters
There were low incidences of grade 3 lipid elevations, and no grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in lipid parameters were reported
Conclusions
⋅ TMC278 was associated with minimal changes in lipid profiles up to Week 48, and may have a potential benefit versus EFV
- there was no difference in the change in ratio of TC/HDL-C among groups.
⋅ No TMC278 dose relationship in lipid parameters. Two 96-week Phase III studies are planned to start Q4 2007.
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|