| |
Bioavailability of Generic Ritonavir and Lopinavir/ritonavir
Tablet Products in a Dog Model
|
| |
| |
Reported by Jules Levin
Kevin W. Garren, PhD; Sibtain Rahim, MD; Kennan Marsh, PhD; John B. Morris, PhD
Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL
2nd International Workshop on HIV Treatment, Pathogenesis and Prevention Research in Resource-Poor Settings · May 20-23, 2008 · Dakar, Senegal
AUTHOR DISCUSSION
· This study demonstrated broad variability in relative bioavailability of generic ritonavir and lopinavir/ritonavir tablet products compared to Norvir capsule and Kaletra tablet, respectively.
· Chemical potency of the generic LPV/r and RTV products was not indicative of plasma levels achieved in these studies.
- In vitro testing, such as chemical potency, is not a reliable predictor of bioavailability of LPV and RTV.
· Based on the previously described experience with dog models, the results of these studies suggest the possibility of decreased bioavailability and reduced clinical effect in humans for some of these generic products.
· The bioavailability of ritonavir and lopinavir in humans from the generic products tested in this work is not known.
AUTHOR CONCLUSIONS
· Significant variability in bioavailability was shown in a dog model amongst generic tablet products containing the Protease Inhibitors RTV and LPV/r.
· Chemical potency of the generic products was not indicative of the plasma levels of RTV or LPV achieved.
· These results reinforce the need for human bioequivalence testing of products containing RTV or LPV/r before being made available to patients.
BACKGROUND
· Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a major worldwide epidemic that has resulted in the death of millions of people.
· In an effort to increase global access for resource limited countries, many agencies support the procurement of both branded and generic antiretroviral medicines, both of which have a role in the global fight against HIV.
· Some quality policies allow for the purchase and distribution of antiretroviral medicines that do not have approval from a stringent regulatory authority or demonstration of human bioequivalence.1
· Commercially available generic ritonavir and lopinavir/ritonavir tablet products manufactured by various pharmaceutical companies were assessed for:
- Chemical potency (amount of the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient [API]).
- Relative bioavailability compared to Norvir capsule and Kaletra tablet using a dog model.
· At the time of testing, both Kaletra and Norvir had FDA approval, EMEA approval and WHO prequalification.
- None of the generic products tested had FDA tentative approval, EMEA approval or WHO prequalification.
· Dog models:
- Are used frequently in formulation development.
- Have been shown to be predictive of bioavailability in humans for specific drugs.2-3
-- Have shown utility for prediction of human bioavailability for lopinavir/ritonavir and ritonavir.
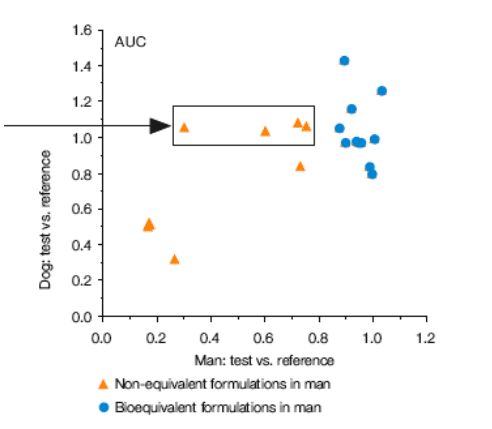
Figure 1. Ritonavir Bioequivalence Studies, Dog vs. Man
· In the model, the results for twelve of sixteen experimental ritonavir formulations in dog mirrored those obtained in man (both bioequivalent and non-bioequivalent results).
· For the remaining four formulations, the good bioavailability observed in the dog was not achieved in man.
· There were no instances in which a formulation that performed poorly in the dog subsequently demonstrated substantial bioavailability in man (Figure 1).
METHODS
· Products were selected for study based on commercial availability. Samples were obtained locally and transported to Abbott's testing laboratories with monitoring devices to ensure the products were not exposed to temperature extremes during the shipping process.
· Five generic products were tested
Generic RTV Products
· Empetus (Emcure)
· Ritomune (Cipla)
Generic LPV/r Products
· Emletra (Emcure)
· Lopimune (Cipla)
· Ritocom* (Hetero)
* Trademark pending
Chemical Potency Assay
· Tablets of each product were tested for chemical potency.
· The API content of LPV or RTV was determined by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with ultraviolet detection.
Bioequivalence Studies in Dogs
· Bioequivalence studies were conducted using a randomized, two-period crossover study design in groups of twelve beagle dogs; each dose was separated by a one-week washout period.
· All doses were administered under fasting conditions.
· Serial blood samples were obtained from each dog over a period of 24 hours after dosing. Concentrations of lopinavir and ritonavir were determined by HPLC-MS/MS following liquid-liquid extraction of the plasma samples.
· Pharmacokinetic parameters, including Cmax and Tmax were obtained from the plasma concentration data for each dog; AUCt was
calculated from the plasma concentration-time profiles.
· Point estimates for Cmax and AUC were calculated on a logarithmic scale for the comparison of the test vs. the reference formulation.
Formulations for Ritonavir (100 mg dose/dog) Bioequivalence Studies
· Reference: Norvir capsule, Abbott Laboratories
· Test: Generic Ritonavir Tablets:
- EmpetusTM, Emcure
- Ritomune, Cipla
Formulations for Lopinavir/ritonavir (200/50 mg dose/dog) Bioequivalence Studies
· Reference: Kaletra tablet, Abbott Laboratories
· Test: Generic Lopinavir/ritonavir Tablets:
- EmletraTM, Emcure
- Lopimune, Cipla
- Ritocom*, Hetero
*Trademark pending
RESULTS
Chemical Potency
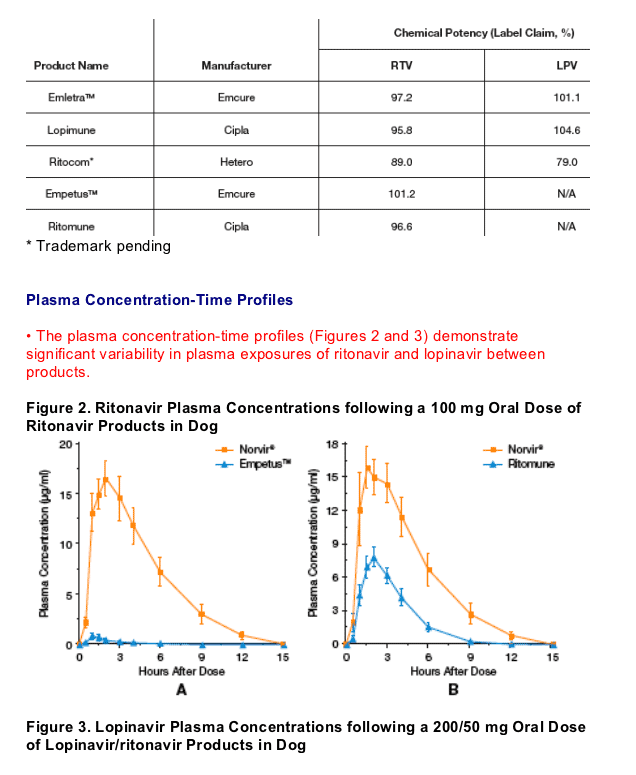
· Chemical potencies of RTV were 96.6% and 101.2% for the RTV products, indicating that the labeled amount of ritonavir was contained in the test ritonavir tablets (Table 1).
· For the LPV/r products, 2 of the 3 generic products showed at least 90% chemical potency. The RTV chemical potencies ranged from 89.0% to 97.2%, and the LPV chemical potencies ranged from 79.0% to 104.6% (Table 1).
Table 1. Chemical Potency of RTV and LPV/r
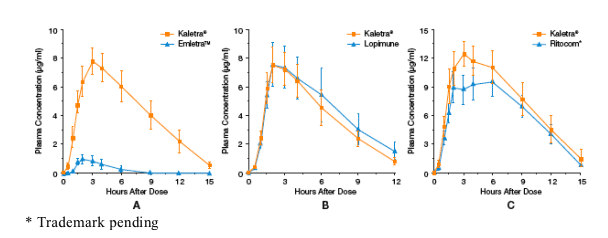
Bioequivalence in Dogs
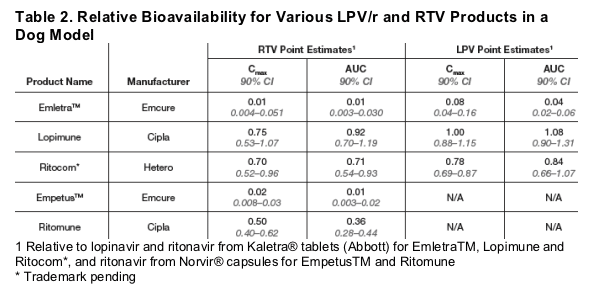
· Relative bioavailability is expressed as point estimates for ritonavir and lopinavir Cmax and AUC for test tablet products compared to the reference products (Table 2).
· Point estimates for RTV AUC in generic RTV tablets compared to Norvir soft gelatin capsule ranged from 0.01 to 0.36.
- Indicating that the bioavailability of these formulations was in the range of 1% to 36% compared to the brand product
· Point estimates for LPV AUC in generic LPV/r tablet products compared to Kaletra tablet, ranged from 0.04 to 1.08.
- Indicating that the relative bioavailability of LPV from generic LPV/r tablets was in the range of 4% to 108% compared to the brand product
REFERENCES
1. The Global Fund. (2007) Global Fund Quality Assurance Policy related to Procurement of Pharmaceutical Products.
2. Akimoto M FA, Nakamura M, et al. (1995) Release and absorption characteristics of chlorphenesin carbamate sustained-release formulations: In vitro-in vivo and in vivo dog-human correlations. International Journal of Pharmaceuticals; 117:31-39.
3. Wu Y LA, Landis E, et al. (2004) The role of biopharmaceutics in the development of a clinical nanoparticle formulation of MK-0869: a Beagle dog model predicts improved bioavailability and diminished food effect on absorption in human. International Journal of Pharmaceuticals; 285:135-146.
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
|