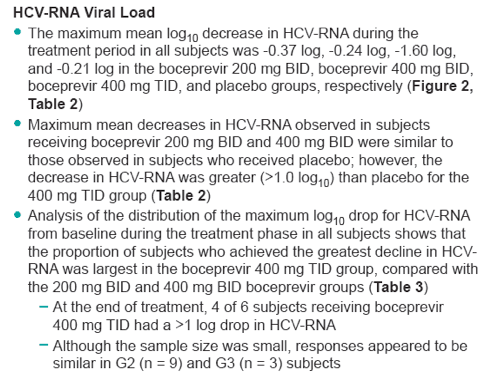
 |
 |
 |
| |
Antiviral Activity of Boceprevir Monotherapy inTreatment-Naive Subjects With Chronic Hepatitis C Genotype 2/3
|
| |
| |
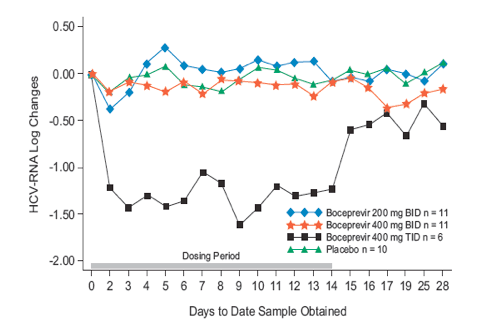
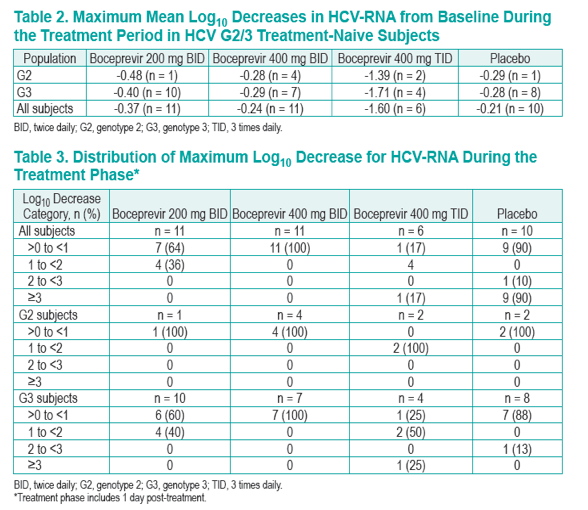
"4 of 6 subjects receiving 400 mg TID had a >1 log drop in HCV-RNA"
Reported by Jules Levin
Presented at the 21st Conference of the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver; February 17-20, 2011; Bangkok, Thailand.
M. Silva,1 C. Kasserra,2 S. Gupta,2 M. Treitel,2 E. Hughes,3 E. O'Mara2
1Hospital Universitario Austral, Pilar, Argentina; 2Merck Research Laboratories, Kenilworth, NJ, USA;3Former employee of Merck Research Laboratories, Kenilworth, NJ, USA
AUTHOR CONCLUSIONS
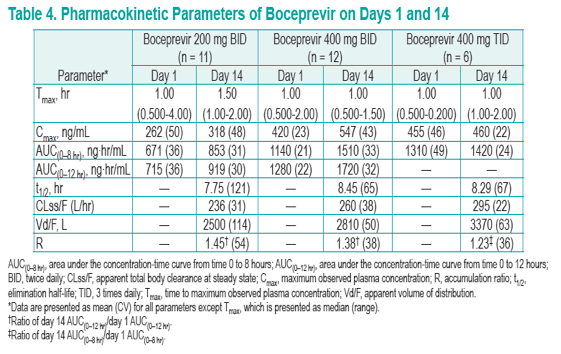
· Boceprevir 400 mg TID is associated with a decrease in HCV-RNA in subjects with HCV G2/3 infection that is comparable to the viral load drop seen in G1 subjects receiving the same monotherapy dose in a previous study
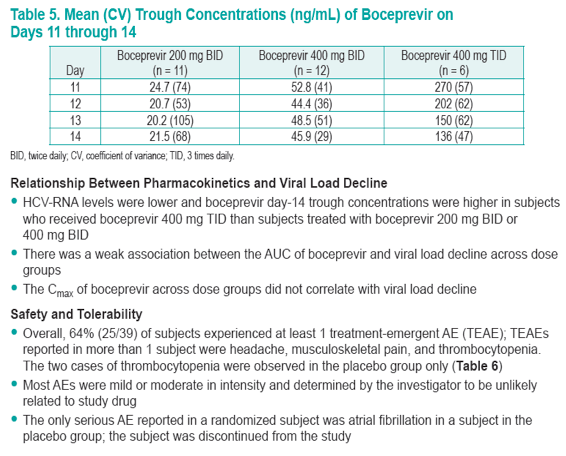
· Boceprevir trough concentrations in the 400 mg TID group were higher than the other BID groups and may be associated with the better viral responses that were observed
· Evaluation of the clinical dose of boceprevir (800 mg TID) as a component of triple therapy for G2/3-infected subjects is of potential clinical interest
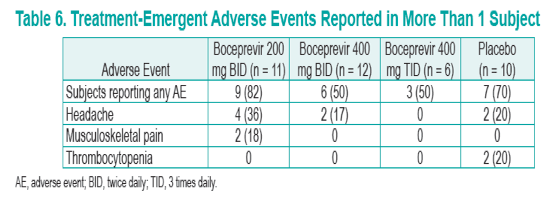
· Overall, boceprevir was well tolerated at doses of 200 mg BID, 400 mg BID, and 400 mg TID
ABSTRACT
Aim: To examine the effect of boceprevir, a novel hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease inhibitor, on HCV-RNA levels in subjects with HCV genotype (G) 2/3 infection.
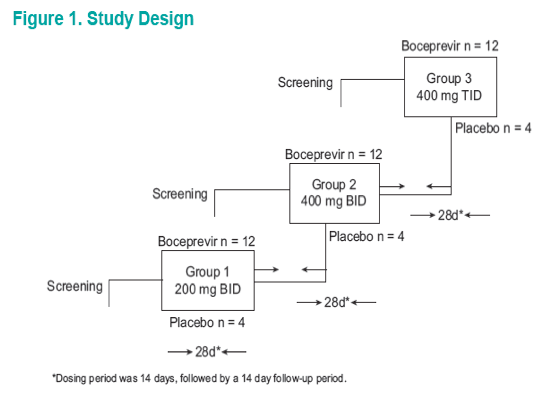
Methods: This was a randomized, placebo-controlled study evaluating the antiviral activity of boceprevir monotherapy 200 mg BID (n = 11), 400 mg BID (n = 12), and 400 mg TID (n = 6) or placebo (n = 10) for 14 days in treatment-naive subjects.
Results: The maximum mean decrease in HCV-RNA was -0.37 log, -0.24 log, -1.60 log and 0.21 log in the 200 mg BID, 400 mg BID, 400 mg TID and placebo groups, respectively. Decreases in HCV-RNA in subjects receiving 200 mg BID and 400 mg BID were similar to placebo; however, the decrease in HCV-RNA in subjects receiving 400 mg TID was markedly different from placebo. At end of treatment, 4 of 6 subjects receiving 400 mg TID had a >1 log drop in HCV-RNA. Although the sample size was small, responses appeared similar in G2 (n = 9) and G3 (n = 30) subjects. Pharmacokinetic analysis revealed a less than dose proportional increase in bioavailability. Overall, boceprevir was well-tolerated.
Conclusion: Boceprevir (400 mg TID) is associated with a decrease in HCV-RNA in subjects with HCV G2/3 infection, comparable to the viral load drop seen in G1 subjects receiving the same monotherapy dose in a previous study. Evaluation of the clinical dose of boceprevir (800 mg TID) as a component of triple therapy for G2/3-infected subjects with detectable HCV RNA at week 4 is of potential clinical interest.
OBJECTIVES
To examine the effect of boceprevir on HCV-RNA levels in treatment-naive subjects with HCV G2/3 infection
To analyze the single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of different boceprevir doses
To characterize the multiple-dose safety and tolerability of boceprevir in this population
METHODS



RESULTS


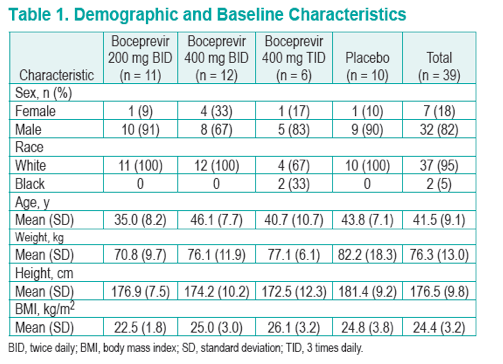
Figure 2. Log10 Mean Change from Baseline in the Overall Population of Treatment-Naive Subjects with Genotype 2 or 3 Infection
References
(1) Te HS, Jensen DM. Epidemiology of hepatitis B and C viruses: a global overview. Clin Liver Dis. 2010;14:1-21, vii.
(2) Alter HJ, Seeff LB. Recovery, persistence, and sequelae in hepatitis C virus infection: a perspective on long-term outcome. Semin Liver Dis. 2000;20:17-35.
(3) Ghany MG, Strader DB, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update. Hepatology. 2009;49:1335-1374.
(4) Shiffman ML, Suter F, Bacon BR et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin for 16 or 24 weeks in HCV genotype 2 or 3. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:124-134.
(5) Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR et al. Peginterferon-α2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:346-355.
(6) No authors. Boceprevir. Drugs R D. 2010;10:203-210.
(7) Bacon B, Gordon SC, Lawitz E, et al.HCV RESPOND-2 final results: high sustained virologic response among genotype 1 previous non-responders and relapsers to peginterferon/ribavirin when re-treated with boceprevir plus Pegintron (peginterferon alfa-2b)/r. Hepatology. 2010;52:430A.
(8) Poordad F, McCone J, Bacon BR, et al. Boceprevir (BOC) combined with peginterferon alfa-2b/ribavirin (P/R) for treatment-naïve patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype (G) 1: SPRINT-2 final results. Hepatology. 52;2010:402A-403A.
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|