 |
 |
 |
| |
Retrospective pooled safety analysis of standard- versus high-dose peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) (PEGASYS) in chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 or 4 patients
|
| |
| |
APASL: Intensified peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) dosing increases sustained virological response rates in genotype 1 hepatitis C patients with elevated low-density lipoprotein - (02/25/11)
Reported by Jules Levin
Presented at The 21st Conference of the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the
Liver (APASL), February 17-20, 2011, Bangkok, Thailand
P. Marcellin,1 S.K. Roberts,2 K.R. Reddy,3 S.A. Harrison,4 D.M. Jensen,5 S.J. Hadziyannis,6 G.J. Dore,7 M. Diago,8 M. Weltman,9 D. Messinger10, F. Tatsch,11 M. Rizzetto12
1Hopital Beaujon, Clichy, France; 2The Alfred Hospital, Prahan, VIC, Australia; 3University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA; 4Brooke Army Medical Center, Fort Sam Houston, TX, USA; 5Center for Liver Diseases, Chicago, IL, USA;
6Henry Dunant Hospital, Athens, Greece; 7National Centre in HIV Epidemiology and Clinical Research, Sydney, NSW, Australia; 8Hospital General de Valencia, Valencia, Spain; 9Nepean Hospital, Sydney, NSW, Australia; 10IST GmbH, Mannheim, Germany;
11Roche, Basel, Switzerland; 12University of Torino, Torino, Italy
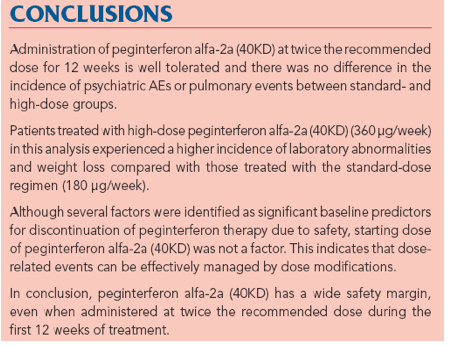
"During the first 12 weeks of treatment, patients in the standard-dose group received a mean cumulative dosage of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) of 2073 μg (range 180-3510 μg, mean 173 μg/week) compared with patients in the high-dose group who received a mean cumulative dosage of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) of 4022 μg (range 360-5040 μg, mean 335 μg/week). The frequency of AEs, SAEs and discontinuations due to safety were similar between the two dosage groups in the first 12 weeks (Table 2; Figure 1)."
"More patients in the high-dose group experienced weight decrease when compared with the standard-dose group (p<0.0001). In addition, the incidence of laboratory abnormalities including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and haemoglobin concentration <100 g/L was more common in patients in the high-dose group.
The incidence of dose modifications of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD), but not of ribavirin, was higher in the high-dose group, while the rate of treatment discontinuation was not different between the two groups.
Significant (p<0.05) baseline predictors for dosage modification of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and of treatment discontinuation due to safety within the first 12 weeks of treatment are shown in Figure 2a and 2b, respectively.
Baseline factors included in the multiple logistic regression as explanatory variables were age, gender, body mass index, HCV genotype, race, histological status, HCV RNA, alanine aminotransferase ratio, platelet count, serum albumin level, creatinine clearance, risk factor for infection and neutrophil count"
INTRODUCTION
The safety profile of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) (PEGASYS) administered at the standard dose of 180 μg/week is well established.
Adverse events (AEs) that are commonly associated with interferon therapy include fatigue, influenza-like symptoms, haematological abnormalities and neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Pulmonary AEs have been associated with interferon; however, these effects are rare and it is unclear whether they are dose-related.[1]
Several recent trials explored treatment responses with a 12 week induction regimen of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) 360 µg/week in difficult-to-cure patients infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV)
OBJECTIVE
The objective of this retrospective analysis was to compare the safety profile of the standard-dose regimen (180 μg/week) with that of the high-dose induction regimen (360 μg/week) of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) administered in combination with ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C.


RESULTS
The standard-dose group comprised a total of 1672 patients, including 94 (5.6%) Asian patients and 98 (5.9%) Black patients, and the high-dose induction therapy group comprised 1268 patients, including 73 (5.8%) Asian patients and 78 (6.2%) Black patients. The demographics of both
groups are shown in Table 1.
During the first 12 weeks of treatment, patients in the standard-dose group received a mean cumulative dosage of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) of 2073 μg (range 180-3510 μg, mean 173 μg/week) compared with patients in the high-dose group who received a mean cumulative dosage of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) of 4022 μg (range 360-5040 μg, mean 335 μg/week).
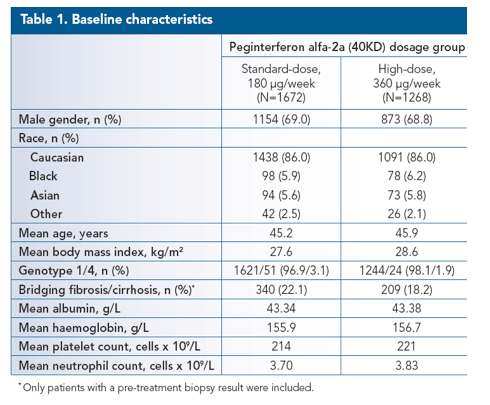
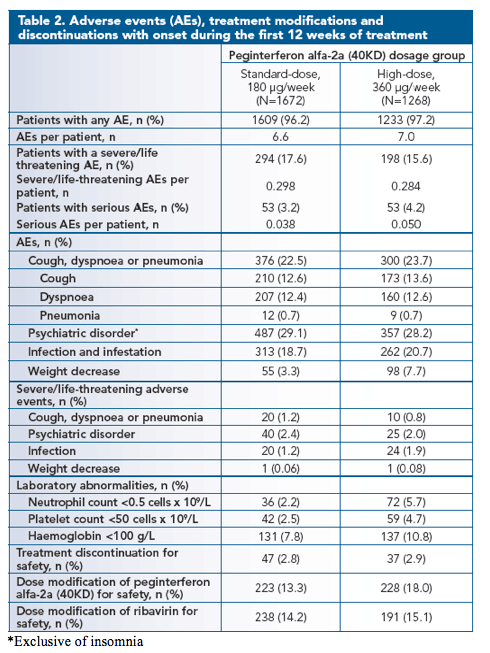
The frequency of AEs, SAEs and discontinuations due to safety were similar between the two dosage groups in the first 12 weeks (Table 2; Figure 1).
*Exclusive of insomnia
The incidence of cough, dyspnoea and psychiatric disorders was comparable between the two dose groups.
The incidence of pneumonia was low and identical in the two dosage groups.
Figure 1. Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for adverse events (AEs), laboratory abnormalities and treatment modifications and discontinuations with onset during the first 12 weeks of treatment. Hazard ratio based on unadjusted Cox proportional hazard model
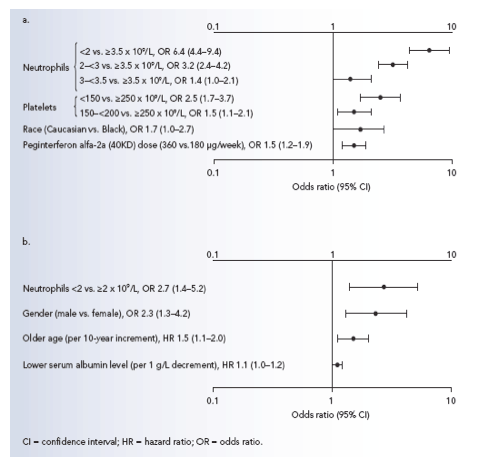
Figure 2. Significant baseline predictors of a) dosage modification of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) for safety reasons and b) treatment discontinuation for safety reasons within the first 12 weeks of treatment by multiple logistic regression (non significant factors included in the multiple logistic regression are not shown).

More patients in the high-dose group experienced weight decrease
when compared with the standard-dose group (p<0.0001). In addition, the incidence of laboratory abnormalities including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and haemoglobin concentration <100 g/L was more common in patients in the high-dose group.
The incidence of dose modifications of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD), but not of ribavirin, was higher in the high-dose group, while the rate of treatment discontinuation was not different between the two groups.
Significant (p<0.05) baseline predictors for dosage modification of
peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and of treatment discontinuation due to
safety within the first 12 weeks of treatment are shown in Figure 2a and 2b, respectively.
Baseline factors included in the multiple logistic regression as explanatory variables were age, gender, body mass index, HCV genotype, race, histological status, HCV RNA, alanine aminotransferase ratio, platelet count, serum albumin level, creatinine clearance, risk factor for infection and neutrophil count
This research was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Basel, Switzerland Support for third-party writing assistance for this presentation was provided by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.

|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|