 |
 |
 |
| |
Neuroprotective MVC Monotherapy in SIV-infected Macaques
|
| |
| |
Reported by Jules Levin
CROI 2011 March Boston
ABSTRACT Paper # 60LB
"MVC monotherapy significantly improved SIV CNS disease outcomes with marked reduction of SIV RNA levels in brain, reduced cellular immune responses, and less neuronal damage. Adding MVC to combined anti-retroviral regimens may effectively treat persistent neurologic disorders in HIV-infected individuals."
K Kelly1, S Beck1, K Pate1, S Queen1, J Karper1, P Tarwater2, L Avery1, W Hubbard1, R Adams1, and Joseph Mankowski*1
1Johns Hopkins Univ, Baltimore, MD, US and 2Texas Tech Univ Hlth Sci Ctr, El Paso, US
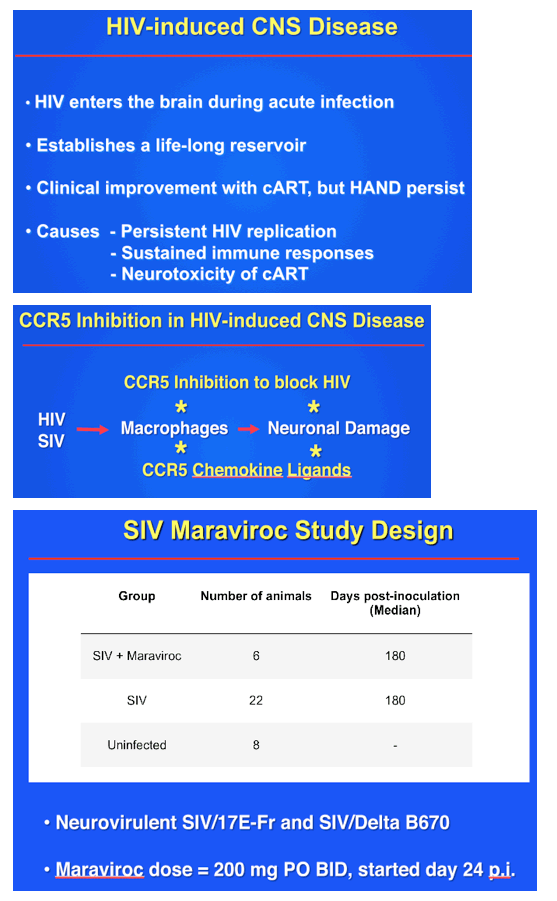
Background: HIV-associated neurologic disorders remain a significant clinical challenge despite combined ART that limits HIV replication. Given the association between HIV-induced central nervous system (CNS) disease and replication of HIV in macrophages in the brain, CCR5 antagonists could attenuate CNS disease both by limiting HIV replication in macrophages and by modulating inflammatory signaling mediated by chemokine-CCR5 interactions. To determine whether the CCR5 antagonist maraviroc (MVC) altered CNS disease progression, simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) -infected animals were treated with MVC and CNS outcomes were compared with untreated SIV-infected animals.
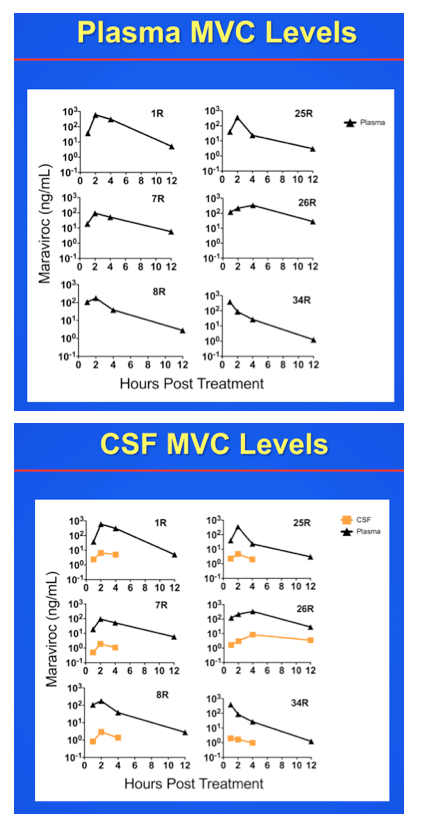
Methods: We inoculated 6 rhesus macaques with SIV/17E-Fr and SIV/DeltaB670 and treated with MVC (200 mg by mouth twice daily) beginning 24 days post-inoculation until the study endpoint 180 days post-inoculation; 22 SIV-infected animals served as untreated, SIV-infected controls; 8 additional animals served as untreated, uninfected controls. MVC levels in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were measured using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectometry. SIV RNA levels in plasma, CSF, spleen, and brain were measured by qRT-PCR. Immunostaining for CD68 and amyloid precursor protein (APP) in the brain was measured by digital image analysis. Group comparisons were performed by the Mann-Whitney test.
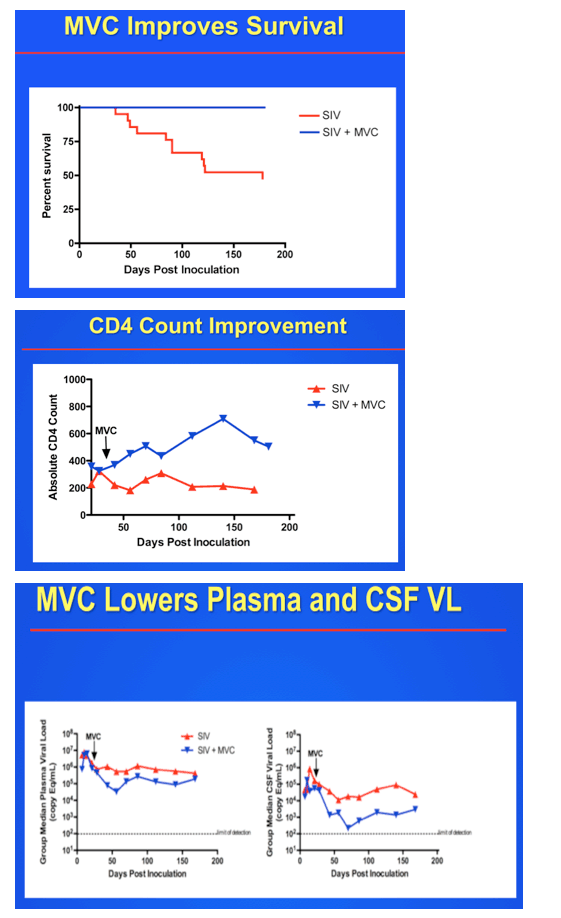
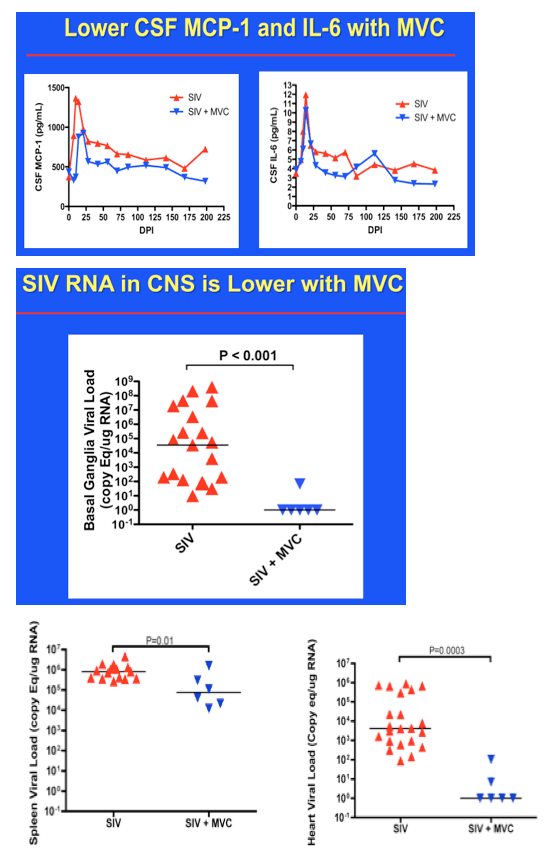
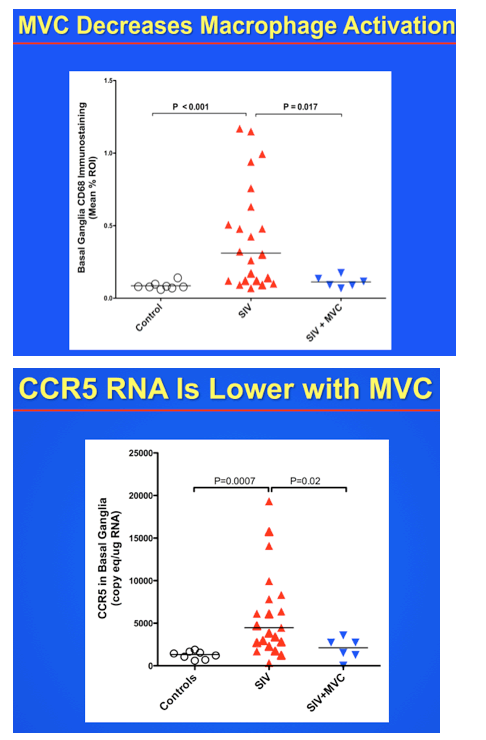
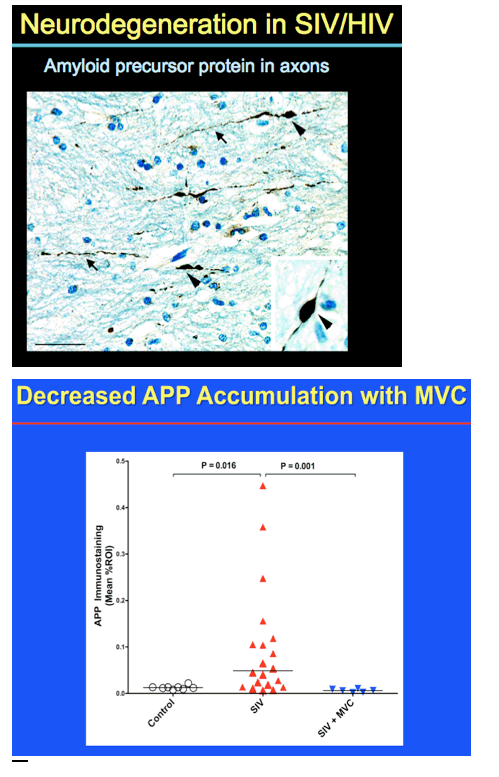
Results: SIV RNA levels in CSF and brain were significantly lower in MVC-treated, SIV-infected macaques vs untreated SIV-infected macaques, demonstrating that MVC monotherapy limits replication of SIV in the CNS. In addition, MVC treatment lowered CNS macrophage activation represented by CD68 immunostaining (p <0.001) and axonal APP immunostaining (p = 0.003) to levels present in uninfected animals. Although maraviroc therapy also reduced plasma viral load and SIV RNA levels in spleen, relative decreases were less substantial than CNS declines, underscoring the need to focus on CNS-specific outcomes in evaluating efficacy of CCR5 inhibition.
Conclusions: MVC monotherapy significantly improved SIV CNS disease outcomes with marked reduction of SIV RNA levels in brain, reduced cellular immune responses, and less neuronal damage. Adding MVC to combined anti-retroviral regimens may effectively treat persistent neurologic disorders in HIV-infected individuals.

|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|