 |
 |
 |
| |
Cystain C - 'Lipid Particle Concentrations and Markers of Renal Disease: SMART' - Unfavorable lipoprotein levels were associated with elevated cystatin C levels, but not with impaired eGFR. Cystatin C may better detect earlier reductions in kidney function
|
| |
| |
Reported by Jules Levin
CROI 2011 Boston March 2
Alison Bormann*1, J Neuhaus1, M Ross2, D Duprez1, and INSIGHT SMART Study Group
1Univ of Minnesota, Minneapolis, US and 2Mt Sinai Sch of Med, New York, NY, US
Background: Dyslipidemia has been associated with an increased risk of developing renal impairment in the general population. Both renal dysfunction and abnormal lipid levels are common in HIV infection. To elucidate the relationship between renal function and lipids, we analyzed apolipoproteins and lipoprotein particles, as well as usual lipids and compared the association of these lipid markers with two measures of renal function in HIV+ participants in the Strategies for Management of Anti-Retroviral Therapy (SMART) trial.
Methods: Stored plasma samples from baseline for 396 participants in SMART were used to centrally measure cystatin C, creatinine, lipoprotein particles, apoplipoproteins A1 and B, and the usual lipids. Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using the MDRD formula. Mean lipid values, and for reference, 2 inflammatory markers, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were compared after adjusting for baseline co-variates for those with a cystatin C level ≥1 vs <1 mg/L (a cystatin C value of ≥1 mg/L has been associated with increased risk of kidney disease) and for those with an eGFR ≥104 and <104 mL/minute/1.73 m2 (a cutoff that gave a comparable percentage with low eGFR to high cystatin C).
Results: Total cholesterol/HDLc and Apo B/A1 ratios were higher (largely due to lower HDL and Apo A1 levels) and total HDL particle concentrations, primarily large HDL particles, were lower for those with higher cystatin C levels (see the table). In contrast, total LDL, primarily small LDL, and total VLDL particle concentrations were higher among those with higher cystatin C levels. hsCRP and IL-6 were also higher in the high cystatin C group. No significant differences were found in the mean lipid measures or inflammatory markers for the high vs low eGFR groups. The correlation of cystatin C and eGFR was -0.40 (p <0.001).
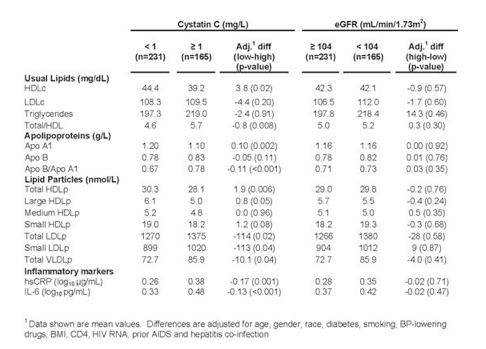
Conclusions: Unfavorable lipoprotein levels were associated with elevated cystatin C levels, but not with impaired eGFR. Cystatin C may better detect earlier reductions in kidney function associated with abnormal lipid concentrations than creatinine-based eGFR measures. Alternatively, alterations in lipid particles and cystatin C levels may both reflect an inflammatory process induced by HIV infection.
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|