 |
 |
 |
| |
Four-week Therapy With Peginterferon Alfa-2b/Ribavirin Effectively Predicts Sustained Virologic Response in Previously Untreated and
Previous-Treatment-Failure Patients With HCV-1 Treated With Boceprevir Plus Peginterferon Alfa-2b/Ribavirin
|
| |
| |
Reported by Jules Levin EASL March 30-Apr 2 2011 Berlin Germany
J.M. Vierling1*, E.J. Lawitz2, F. Poordad3, M.S. Sulkowski4, M. Bourliere5, M. Buti6, C. Cooper7, J.S. Galati8, J.K. Albrecht9, N. Boparai9, C.A. Brass9, M. Burroughs9, V. Sniukiene9, S. Bruno10
1Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, USA, 2Alamo Medical Research, San Antonio, TX, USA, 3Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 4Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5Fondation Hopital Saint Joseph, Marseille, France, 6Vall d'Hebron University Hospital, Barcelona, Spain,
7Ottawa Hospital, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 8Liver Specialists of Texas, Houston, TX, USA, 9Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 10A.O. Fatebenefratelli e Oftalmico, Milan, Italy; *vierling@bcm.edu

BACKGROUND
In Phase 3 studies, addition of boceprevir (BOC), an HCV NS3
protease inhibitor, to peginterferon (P) and ribavirin (R) in
previously untreated and previous-treatment-failure patients
with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 (HCV-G1) produced superior
sustained virologic response (SVR) rates than standard of care
treatment with P/R.
In the clinical trials, a 4-week P/R lead-in period preceded the
addition of BOC to the P/R treatment regimen.
Potential clinical benefits of 4-week P/R lead-in HCV-G1 patients:
-- Reduction of viral load prior to introduction of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agent
-- Prevention of exposure to DAA agents in patients who cannot tolerate P/R therapy
-- Accurate assessment of interferon responsiveness - strongest predictor of SVR
-- Determination of tolerance to and compliance with P/R
therapy
-- Assessment of risk vs benefit when decision to treat unclear
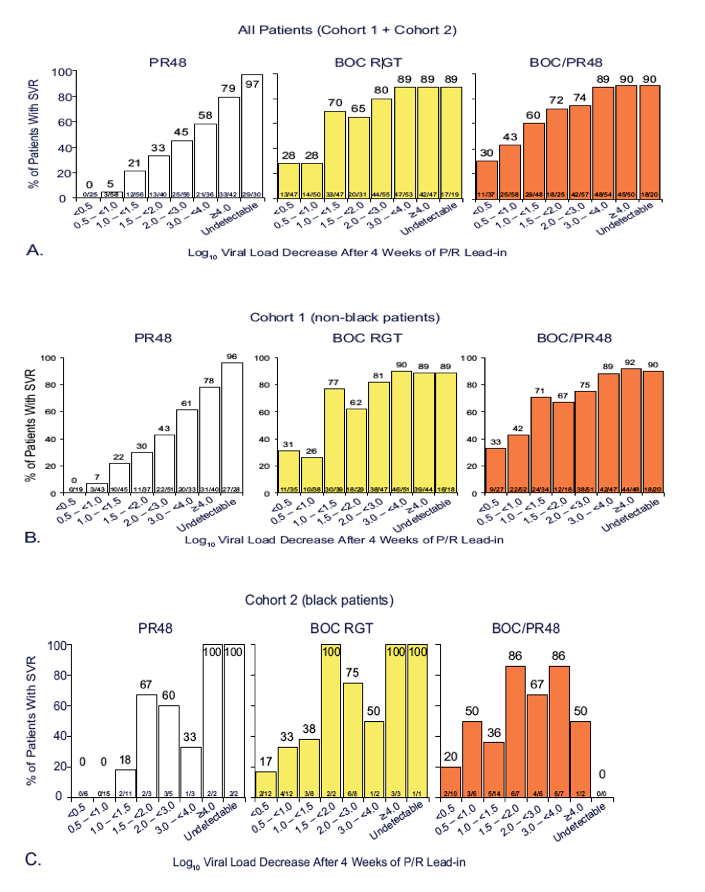
In a large Phase 3 study of genotype 1-infected patients treated
with peginterferon alfa-2a or 2b (~3000 patients), classification
and regression tree analysis demonstrated that a cut-off at
~1.0 log10 decline best predicts SVR (McHutchison et al. N Engl
J Med. 2009;361:580-593).
In a Phase 2 study of BOC (SPRINT-1), patients with a <1.0
log10 decrease in viral load after 4 weeks of P/R were less likely
to achieve SVR than were those with a ≥1.0 log10 decrease in
viral load after 4 weeks of P/R (SVR 38% vs 75%) (Kwo et al.
Lancet. 2010;376:705-716).
PURPOSE
To assess the relationship between the degree of interferon response after 4 weeks of P/R lead-in therapy and SVR with or without the
addition of BOC
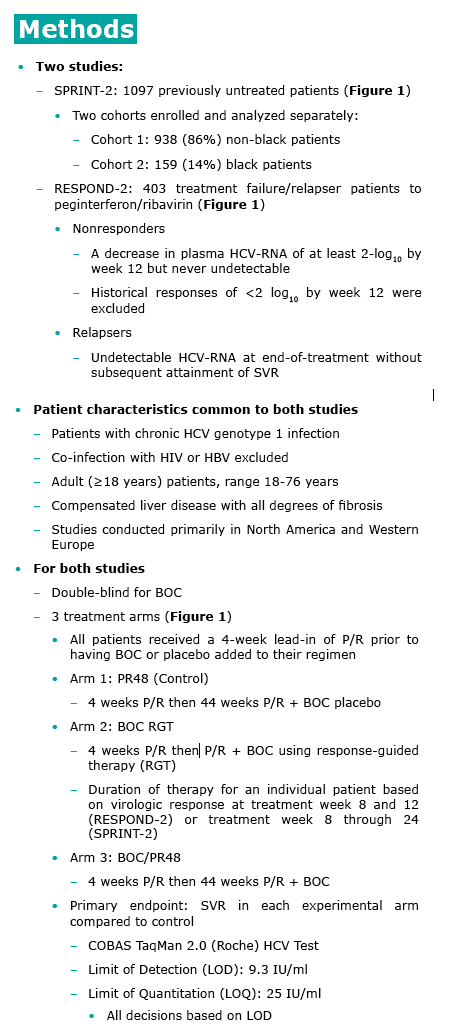
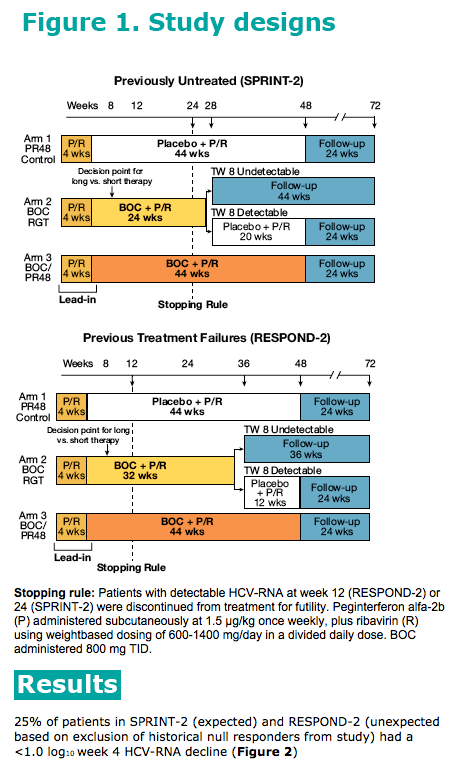
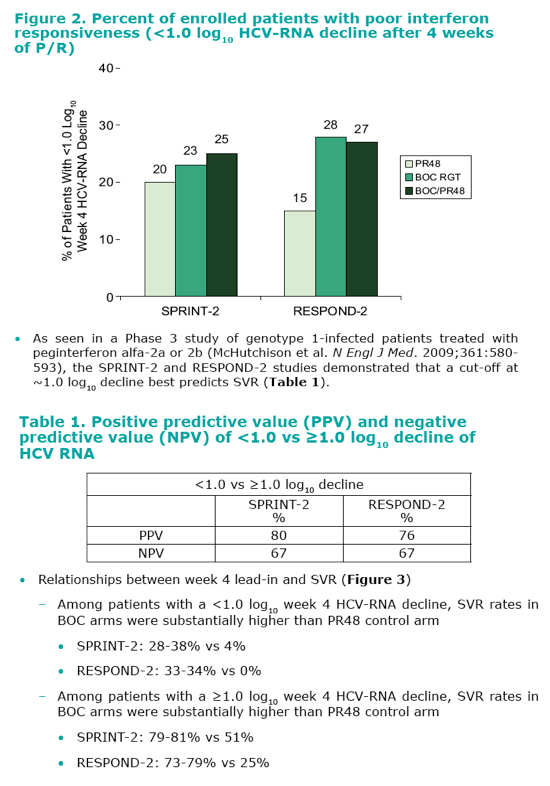
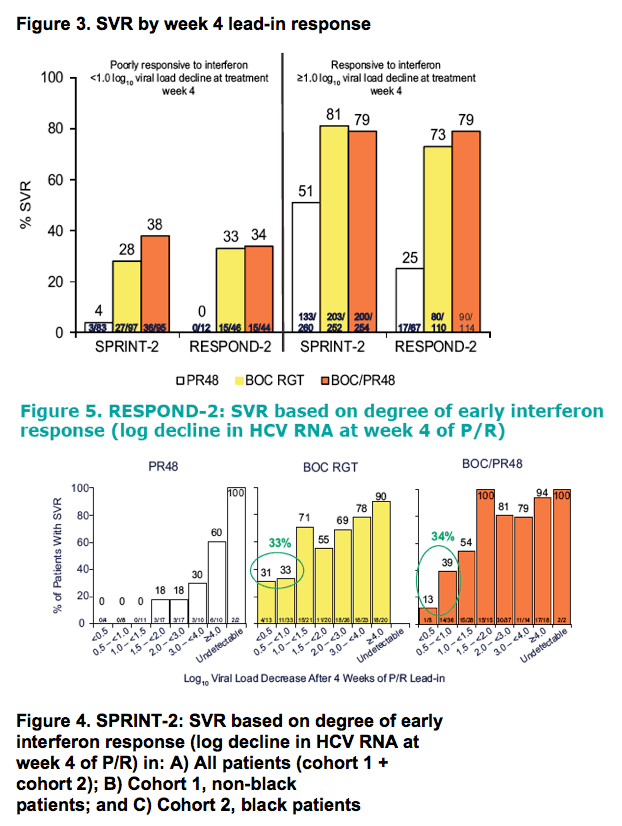
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|