 |
 |
 |
| |
ICAAC: Pigtailed Macaques Under High Doses of Depot Medroxyprogesterone are Protected from Multiple SHIV Exposures with a Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Intravaginal Ring
|
| |
| |
The combination of successes (e.g. Partners in Prevention and CAPRISA 004) with unanticipated disappointing results (e.g. VOICE) in recent oral and topical clinical PrEP trials highlights the critical importance of designing strategies that are not only effective and safe, but also acceptable and likely to result in a high level of adherence. Sustained release devices such as intravaginal rings (IVRs) provide women with a coitally independent option. Developed under funding from the NIH and CDC, a polyurethane reservoir ring was designed to deliver the prodrug, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), which is more potent in vitro than tenofovir. The authors previously presented their findings at CROI 2013 in which the TDF IVR (which was inserted monthly over a 5 month period) protected 6/6 non-human primates (NHP) from 16 weekly challenges with SHIV compared to 5/6 control animals that became infected after an average of 4 weekly exposures. At ICAAC 2013 (Sept 10-13) in a late-breaker session, the authors presented new findings in which they tested the efficacy of the TDF IVR compared to a Placebo IVR in NHP treated monthly with Depo Provera.
Epidemiological studies suggest that this common form of contraception may be associated with increased risk of HIV. Thus, the goal of this new study was to develop a more stringent NHP model and test the efficacy and safety of the TDF IVR under conditions that may simulate women using Depo Provera.
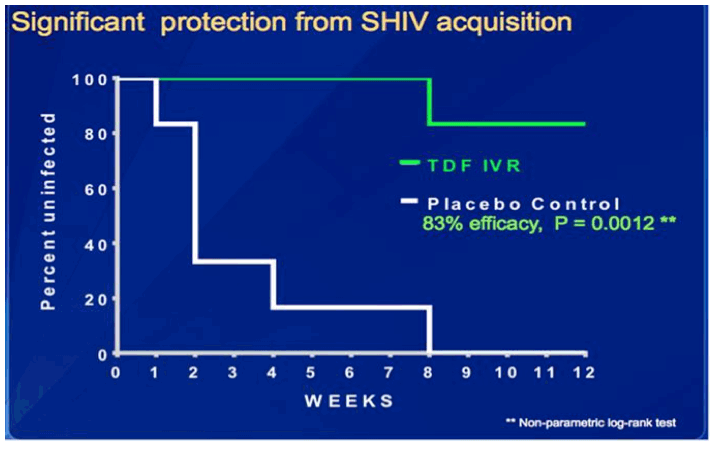
Sexually mature pigtailed macaques have been used extensively for modeling topical vaginal PrEP because of their similarities to women in vaginal architecture, vaginal microflora, and a monthly menstrual cycle, with an average cycle being 28-32 days. In the study described here, six placebo and six TDF IVR animals were treated with high dose Depo Provera (30mg) every six weeks, starting four weeks before the first virus exposure. Animals were exposed to virus once weekly for 12 weeks to mimic multiple exposures in women. Rings were changed every 4 weeks.
All of the placebo animals became infected with a median of two exposures to infection. In contrast, 5/6 NHP remained uninfected through 12 exposures (83% efficacy, P=0.0012). One TDF IVR treated NHP became infected after the 8th virus exposure. The rings were well tolerated in all animals. This is the first study to test efficacy and safety of PrEP in this high dose Depot Provera NHP model, which may prove to be a more rigorous model of susceptibility and better inform clinical trial design in women using injectable hormonal contraception, the most common form of contraception being used globally.
The TDF IVR is being advanced into a human Phase I clinical trial.
Betsy Herold, Albert Einstein Coll. of Med., Bronx, NY.
James Smith, Lab. Branch, DHAP, NCHHSTP, CDC, Atlanta, GA
ICAAC: Tenofovir Vaginal Ring Protects 5 of 6 Macaques From SHIV After High-Dose Depo-Provera - Written by Mark Mascolini - (09/18/13)
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|