 |
 |
 |
| |
Twice-Daily TAF May Be Option With Rifampin for TB and HIV
|
| |
| |
16th European AIDS Conference, October 25-27, 2017. Milan
Mark Mascolini
Twice-daily tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) with the anti-TB agent rifampin yielded TAF and tenofovir-diphosphate (TFV-DP) levels similar to those seen with once-daily TAF without rifampin in a study in healthy volunteers [1]. The results position twice-daily TAF plus rifampin for further study in people coinfected with TB and HIV.
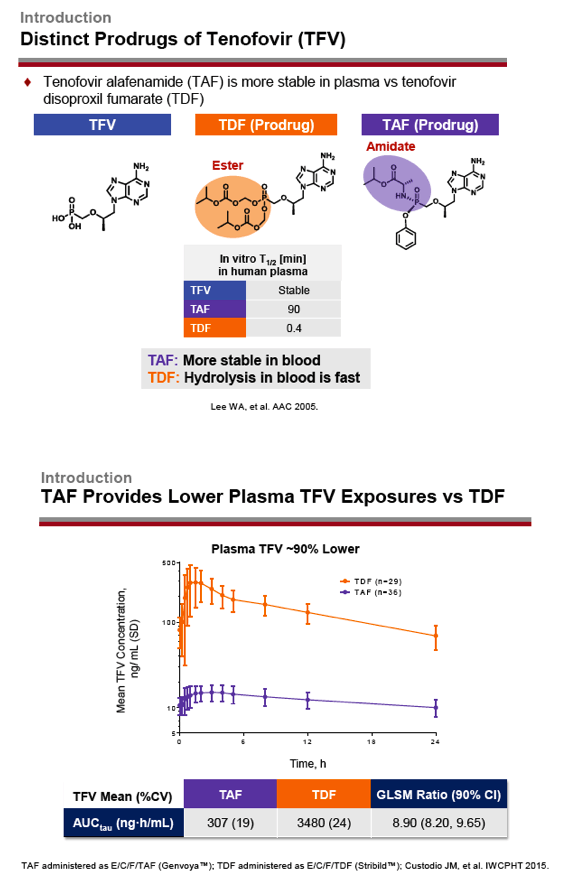
TAF and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) are distinct prodrugs of tenofovir. Because TAF loads efficiently into target cells, it results in lower tenofovir exposure in plasma and does not affect kidney and bone markers as much as TDF. Once-daily TAF is licensed for HIV infection with other antiretrovirals, including single-tablet coformulations.
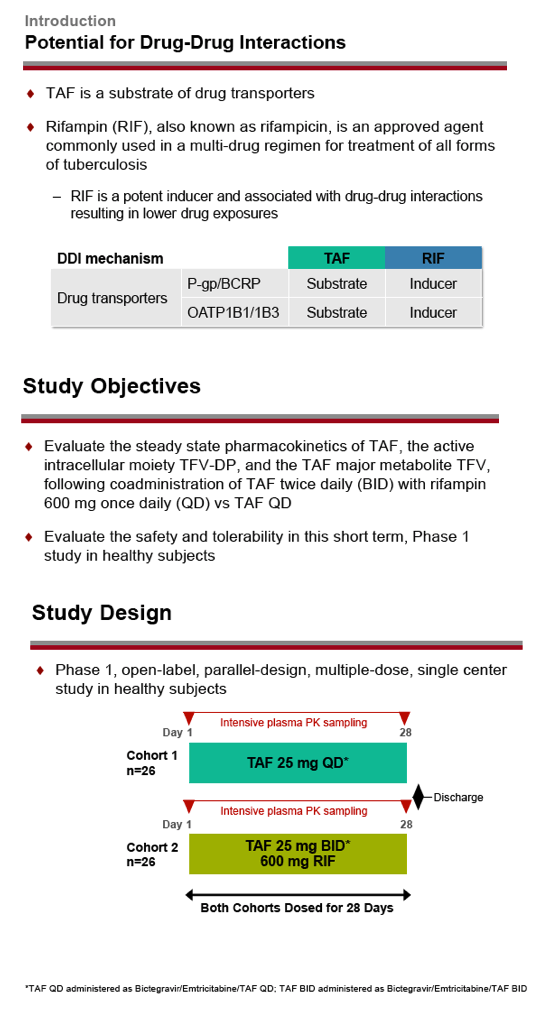
Rifampin, a central component of anti-TB regimen, is a potent inducer of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters and thus lowers exposure of numerous drugs. TAF is a substrate of drug transporters P-gp, BCRP, and OATP1B1/1BC, which rifampin induces. Once-daily TAF is not indicated for use with rifampin, whereas once-daily TDF is.
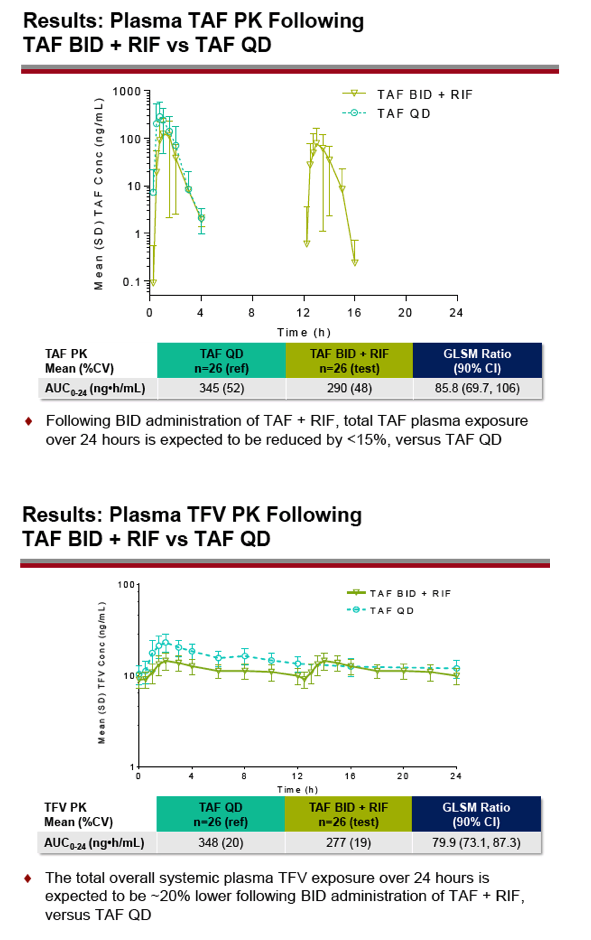
Gilead Sciences researchers conducted this study to compare pharmacokinetics of TAF and TFV-DP when TAF is given twice daily with rifampin versus once daily without rifampin. The analysis involved two groups of 26 healthy volunteers, one taking once-daily TAF as part of single-tablet bictegravir/emtricitabine/TAF (50/200/25 mg) and one taking twice-daily TAF (2 x 25 mg) with bictegravir/emtricitabine. The twice-daily TAF group also took 600 mg of rifampin once daily. Researchers compared TAF and TFV-DP exposure in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with twice-daily versus once-daily TAF by calculating geometric least-squares mean (GLSM) ratios and 90% confidence intervals (CI).
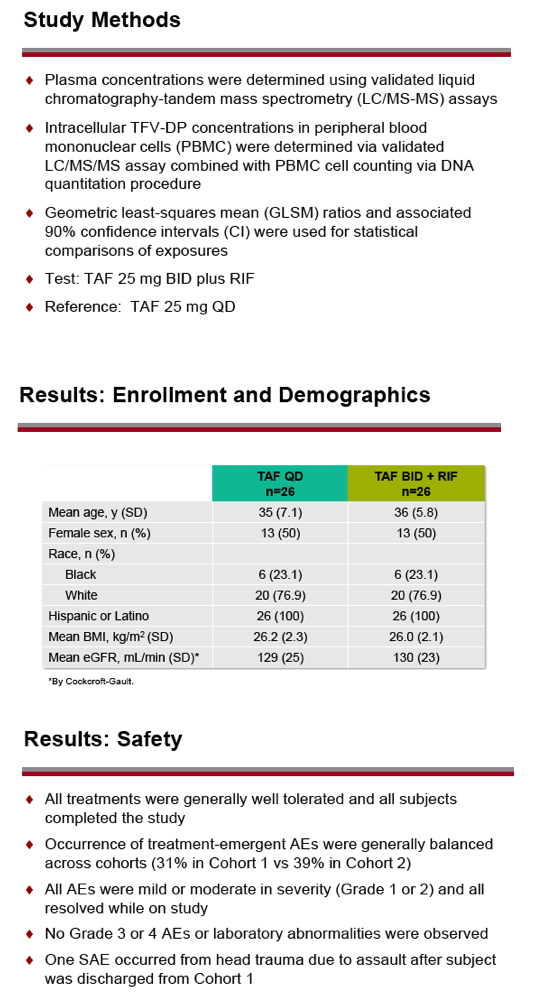
The once-daily and twice-daily TAF groups averaged 35 and 36 years in age. Half in each group were women, and 6 in each group (23%) were black. Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) averaged 129 mL/min in the once-daily group and 130 mL/min in the twice-daily group, and both groups averaged around 26 kg/m(2) in body mass index. All adverse events were grade 1 or 2 and all resolved during the study. One serious adverse event was not related to study drugs (head trauma from assault). All volunteers completed the 28-day study.
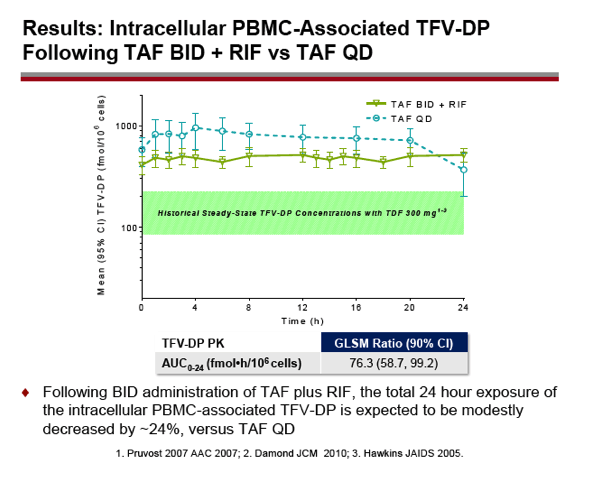
Twice-daily TAF with rifampin yielded TAF plasma exposure about 14% lower than once-daily TAF without rifampin (GLSM ratio for 24-hour area under the concentration-time curve [AUC] 85.8, 90% CI 69.7 to 106). Total overall systemic TFV exposure was about 20% lower with twice-daily TAF plus rifampin than with once-daily TAF without rifampin (GLSM ratio for AUC 79.9, 90% CI 73.1 to 87.3). Total 24-hour TFV-DP exposure in PBMCs was about 24% lower with twice-daily TAF than with once-daily TAF (GLSM ratio for AUC 76.3, 90% CI 58.7 to 99.2).
Gilead researchers concluded that TAF and TFV-DP levels with twice-daily TAF plus rifampin should be similar to those attained with once-daily TAF without rifampin, which are known to be efficacious and safe. They proposed that TAF at a dose of 25 mg twice daily with rifampin "may provide a suitable option for patients with HIV-TB coinfection," pending results of further studies.
Reference
1. Custodio JM, West S, Lutz J. Twice daily administration of tenofovir alafenamide in combination with rifampin: potential for tenofovir alafenamide use in HIV-TB coinfection. 16th European AIDS Conference. October 25-27, 2017. Milan. Abstract PS13/4.
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|