 |
 |
 |
| |
HIGH PREVALENCE OF FATTY LIVER DISEASE [FLD] AND ADVANCED FIBROSIS IN AN URBAN MULTIETHNIC US COHORT OF PERSONS WITH HIV
|
| |
| |
AASLD 2020 Nov 11-16
Samer Gawrieh1, Jordan E. Lake2, Paula Debroy3, Julia A. Sjoquist4, Montreca Robison1, Fatih Akisik5, Surya S. Bhamidipalli6, Chandan K. Saha6, Kimon Zachary4, Gregory K. Robbins4, Samir K. Gupta6, Naga P. Chalasani1, Raymond T. Chung7 and Kathleen E. Corey8, (1)Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Indiana University School of Medicine, (2) University of Texas - Houston, (3)University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, (4)Massachusetts General Hospital, (5)Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, (6)Indiana University School of Medicine, (7)Liver Center, Gastroenterology Division, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, (8)Division of Gastroenterology, Massachusetts General Hospital
abstract
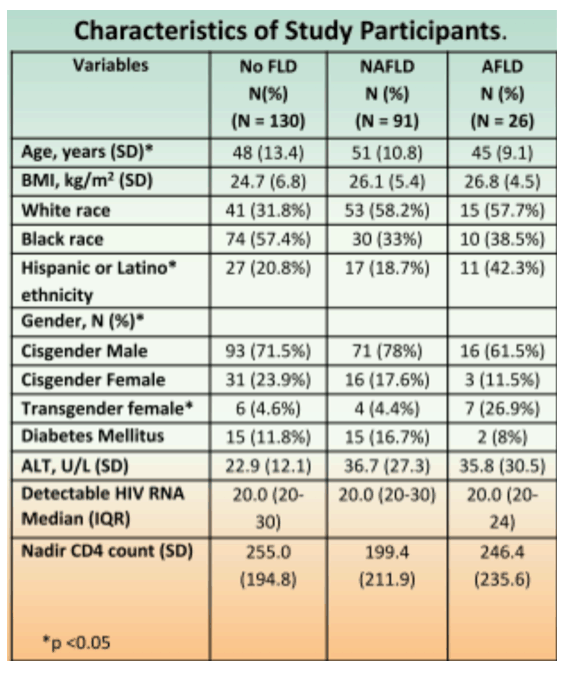
Background: Fatty liver disease (FLD) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality among persons with HIV (PWH), yet the current prevalence of FLD due to alcoholic (AFLD) and non-alcoholic (NAFLD) origins in PWH in the United States (US) is not well defined.
Methods: Participants in outpatient HIV clinics in 3 US centers underwent simultaneous liver ultrasound (LUS) and vibration-controlled transient elastography by FibroScan to measure controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) and liver stiffness measurement (LSM) . Alcohol use was assessed with the NIAAA and AUDIT questionnaires. AFLD was defined as FLD in a person with AUDIT score ≥8. The prevalence of AFLD, NAFLD, advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis (Siddiqui et al CGH 2018) were determined.
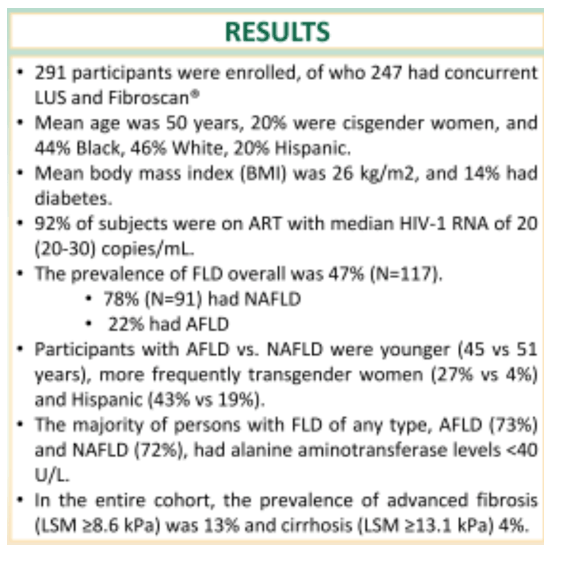
Results: 291 participants enrolled. The mean age was 50 years, 20% were cisgender women, and 44% Black, 46% White, 20% Hispanic. The mean body mass index was 26 kg/m2, and 14% had diabetes; 92% were on ART with median HIV-1 RNA of 20 copies/mL. Of 247 patients who completed LUS, the overall prevalence of FLD was 47% (N=117). Of those with FLD, 78% (N=91) had NAFLD and 22% had AFLD . Participants with AFLD vs. NAFLD were younger (45 vs 51 years), more frequently transgender women (27% vs 4%) and Hispanic (43% vs 19%). The majority of persons with FLD of any type (AFLD 73%, NAFLD 72%), had alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels <40 U/L. In the entire cohort, the prevalence of advanced fibrosis (LSM ≥8.6 kPa) was 13% and cirrhosis (LSM ≥13.1 kPa) 4%.
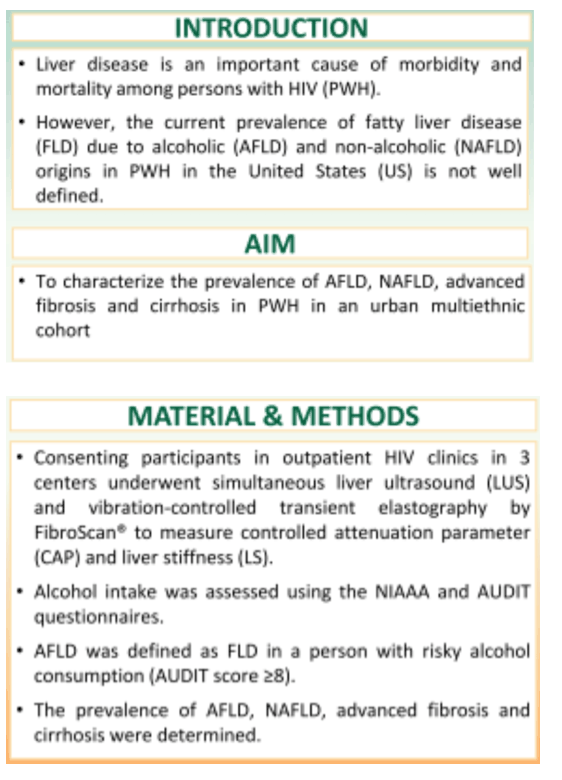
Conclusion: Nearly half of PWH seen in outpatient urban clinics have FLD, the majority with normal ALT levels. Of those with FLD, NAFLD accounts for the majority of cases (80%) while 20% resulted from AFLD. 13% of those with FLD had advanced fibrosis and 4% had cirrhosis. Data highlight the significant burden of AFLD, NAFLD and advanced fibrosis in this population.
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|