 |
 |
 |
| |
SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF REMDESIVIR IN A PEDIATRIC COVID-19 POPULATION
|
| |
| |
CROI 2021 March 6-10 Reported by Jules Levin
Flor Munoz1, William Muller2, Amina Ahmed3, David Kimberlin4, Ana Mendez- Echevarria5, Janet S. Chen6, Mari Nakamura7, William Pomputius8, Zongbo Shang9, Henry N. Hulter9, Catherine O'Connor9, Heather Maxwell9, Kathryn Kersey9, Diana Brainard9, Pablo Rojo10
1Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, USA, 2Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA, 3Levine Children's Hospital at Atrium Health, Charlotte, NC, USA, 4University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, USA, 5La Paz University Hospital, Madrid, Spain, 6Drexel College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, USA, 8Children's Minnesota Hospital, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 9Gilead Sciences, Inc, Foster City, CA, USA, 10Hospital 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain
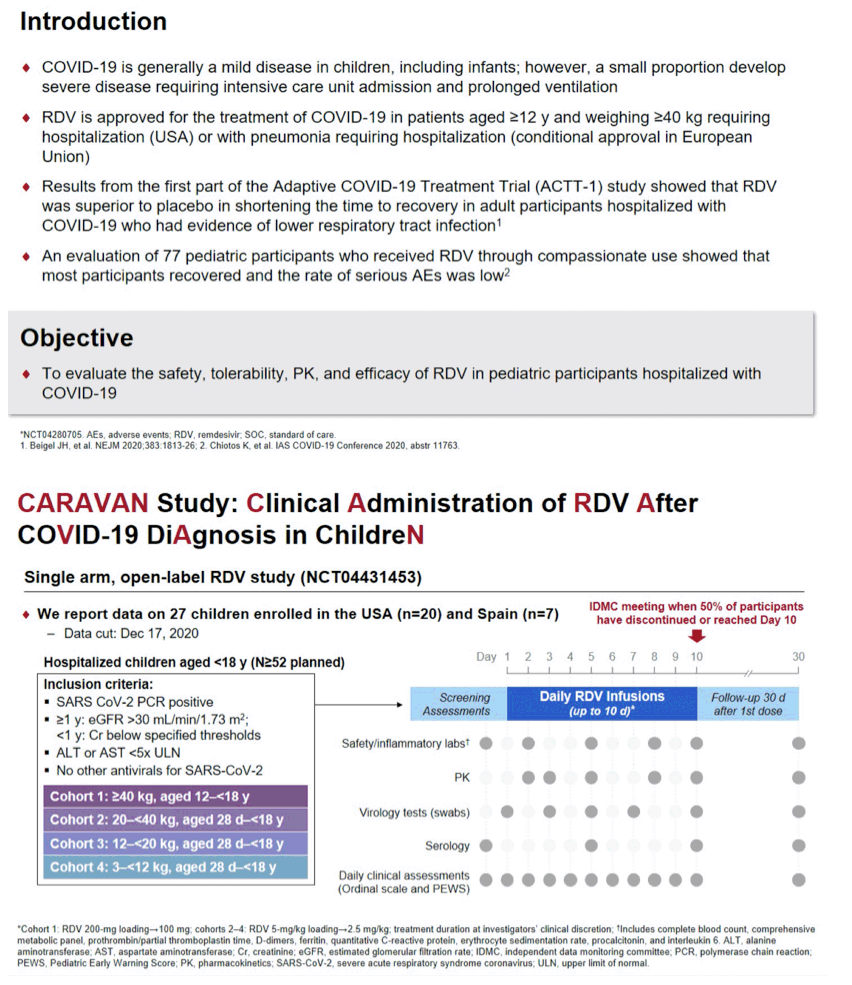
Background: COVID-19 is generally a mild disease in children and infants. However, a small proportion develop severe disease requiring intensive care and ventilatory support. Remdesivir (RDV), a direct-acting nucleotide pro-drug inhibitor of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases, has been shown to shorten time to recovery in adults with severe COVID-19. The aim of this study is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of RDV in pediatric patients.
Methods: CARAVAN (NCT04431453) is an ongoing open-label study of RDV in hospitalized pediatric patients with PCR-confirmed COVID-19. IV RDV is given for up to 10 days: 200mg on Day 1 followed by 100mg daily in Cohort 1 (12 to <18y, weight ≥40kg) or 5mg/kg on Day 1 followed by 2.5mg/kg daily in Cohorts 2-4 (28 days to <18y, stratified by weight). Safety is assessed by adverse events (AEs) and laboratory tests. Efficacy assessments include change in oxygen requirements and clinical status on a 7-point ordinal scale through Day 10.
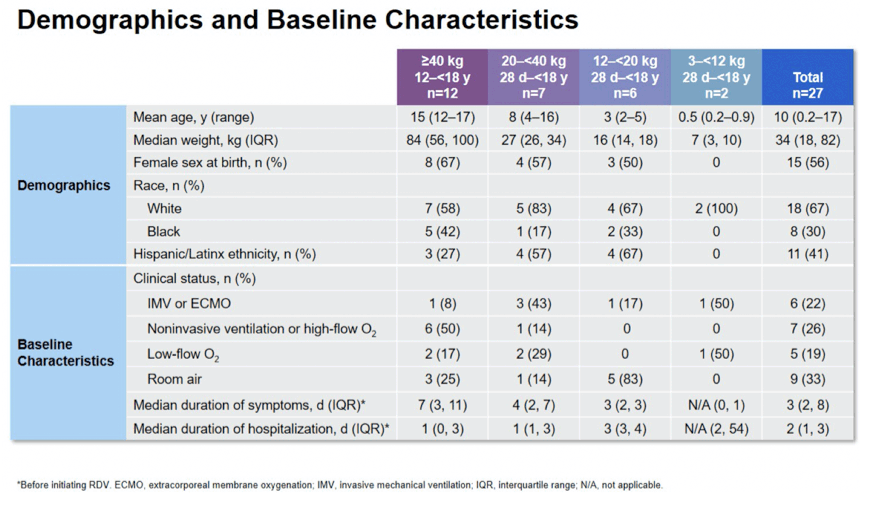
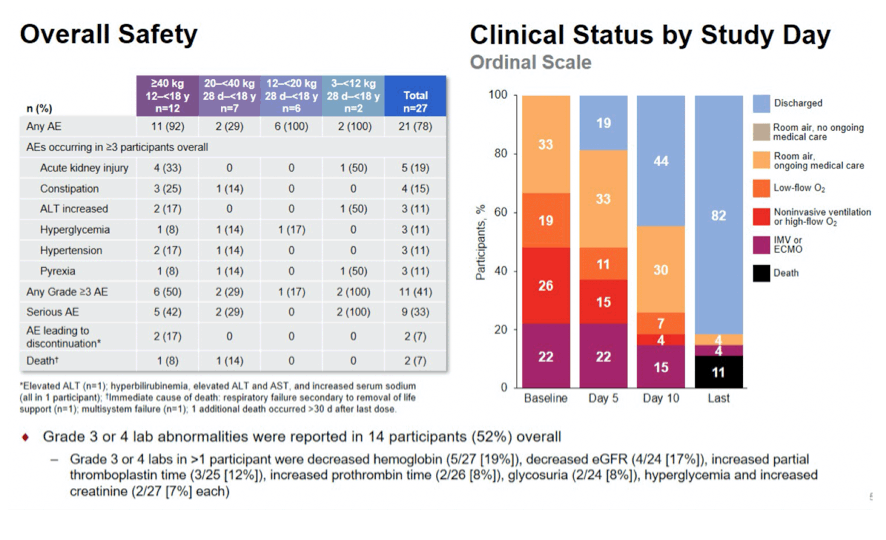
Results: Preliminary results for the first 27 patients are presented. Median (range) age and weight were: Cohort 1, 15 (12-17)y and 84 (47-192)kg; Cohort 2, 8 (4-16)y and 27 (25-39)kg; Cohort 3, 3 (2-5)y and 16 (12-18)kg; Cohort 4, 6 (2-11)m and 7 (3-10)kg. Overall, 52% were <12y, 56% were female, and 96% had ≥1 comorbid medical condition. Median number of RDV doses was 5; most RDV discontinuations were due to clinical improvement. At baseline, 67% required supplemental oxygen, including 22% on invasive ventilation; at Day 10, the values were 26% and 15%, respectively. In total, 70% showed clinical improvement on the 7-point ordinal scale at Day 10. Most (78%) had ≥1 AE, including 17% with study drug-related AEs; 7% discontinued study drug due to an AE. Serious AEs were reported for 33% of patients; no SAEs were study drug related. Two patients died within 30 days of completing treatment. Grade 3 or 4 lab abnormalities were reported in 52%; those reported in ≥1 patient were decreased hemoglobin (n=5), and hypoglycemia, glycosuria, and increased PTT (n=2 each). No safety trends related to RDV were apparent.
Conclusion: Among pediatric patients aged 2m to 17y treated with RDV for COVID-19, 70% had clinical improvement. The study is ongoing; enrolment of full term and preterm neonates is pending determination of the dose to be evaluated.
|
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|