| |
Behavioral and Clinical Characteristics of Persons Living with Diagnosed HIV Infection-Medical Monitoring Project, United States, 2019 Cycle
|
| |
| |
At year-end 2018, an estimated 1,040,352 persons in the United States and 6 dependent areas were living with diagnosed HIV infection [1]. In 2019, the number of new HIV diagnoses was 37,881 [1]. Although the National HIV Surveillance System (NHSS) collects information about persons with diagnosed HIV infection [2], other surveillance systems provide more detailed information about care seeking, health care use, use of ancillary services, and other behaviors [3]. the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) implemented the Medical Monitoring Project (MMP), which from 2009 to 2014 collected data from a 3-stage probability sample of adults receiving HIV medical care [5]............
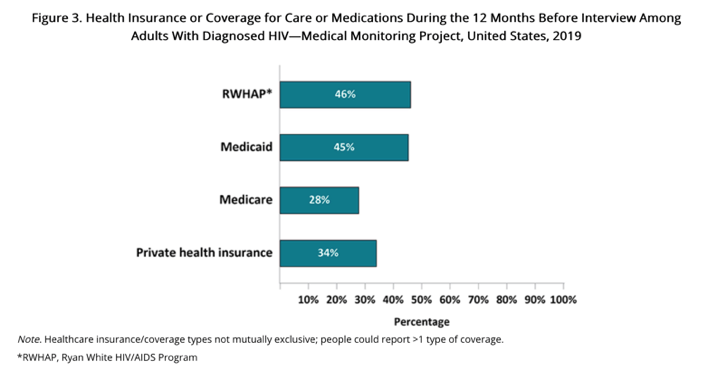
Over half (57%) had more than a high school education and 85% were born in a U.S. state or territory. The estimated prevalence of homelessness among all persons with diagnosed HIV was 9%. Approximately 13% had moved in with other people because of financial problems, and 3% had been evicted from housing during the past 12 months. An estimated 98% had health insurance or coverage for care or medications (including antiretroviral therapy [ART] medications): 46% had coverage through the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program, 45% had Medicaid, 28% had Medicare, and 34% had private health insurance (Figure 3). An estimated 43% had a disability, 41% were unemployed, and 42% had household incomes at or below the federal poverty threshold. An estimated 18% received Supplemental Security Income (SSI), and 21% received Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Indicators
The estimated prevalence of homelessness among persons who received outpatient HIV care in the past 12 months was 9% (Table 22). The median HIV stigma score (see the appendix for more details on how the score was derived and its validity) among all persons was 38. When the personalized stigma dimension was limited to the past 12 months, the median HIV stigma score was 31. An estimated 7% of persons engaged in high-risk sex. HIV stigma: HIV stigma since HIV diagnosis was defined as the median score on a 10-item scale ranging from 0 (no stigma) to 100 (high stigma) that measures 4 dimensions of HIV stigma: personalized stigma since HIV diagnosis, current disclosure concerns, current negative self-image, and current perceived public attitudes about people living with HIV [11]. HIV stigma during the past 12 months was defined as the median score on a 10-item scale ranging from 0 (no stigma) to 100 (high stigma) that measures 4 dimensions of HIV stigma during the past 12 months: personalized stigma during the past 12 months, current disclosure concerns, current negative self-image, and current perceived public attitudes about people living with HIV.
link to report:
https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/library/reports/hiv-surveillance-special-reports/no-28/content/commentary.html
Clinical Characteristics
According to the CDC stage of disease classification for HIV infection [10], an estimated 57% of persons ever had stage 3 (AIDS) disease (Table 3). An estimated 8% of persons had a geometric mean CD4 T-lymphocyte (CD4) count of 0–199 cells/μL. The estimated average geometric mean CD4 count among all persons was 637 cells/μL, and the median geometric mean CD4 count was 602 cells/μL (range, 1–2,650) (data not shown in table).
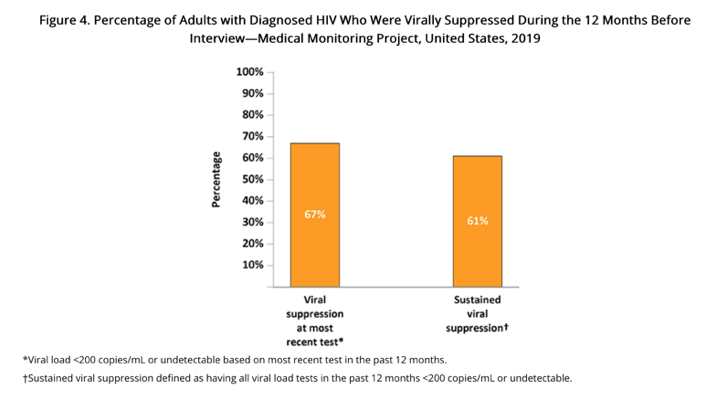
An estimated 67% of persons had an undetectable (< 200 copies/mL) viral load at the most recent measurement, while 61% had undetectable viral loads at all measurements during the past 12 months (sustained viral suppression) (Figure 4; Table 3).
Use of Health Care Services
Overall, 97% had received outpatient HIV care during the past 12 months (Figure 5; Table 4). An estimated 79% were retained in care during the past 12 months, while 61% were retained in care during the past 24 months. An estimated 83% of persons had an ART prescription documented in the medical record during the 12 months before interview. Of persons who met the clinical criteria for Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) prophylaxis, 33% had a prescription for PCP prophylaxis documented in the medical record.
Among sexually active persons, an estimated 50% were tested for gonorrhea, 51% for chlamydia, 65% for syphilis, and 45% for all 3 sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) (Figure 6; Table 5).
An estimated 42% of persons were seen in an emergency department at least once, and 4% were seen at least 5 times (Figure 7; Table 6). An estimated 19% of persons were admitted to a hospital for an illness at least once.
Self-reported ART Medication Use and Adherence
An estimated 98% of persons had ever taken ART and 94% of persons were currently taking ART, based on self-report (Table 7). Among the estimated 4% of persons with a history of ART use but who were not currently taking ART, 51% were not taking ART due to money or insurance problems and 29% were not taking ART because the person’s health care provider never discussed restarting ART with them (Table 7).
Among persons taking ART, 61% took all of their ART doses in the past 30 days (Table 8). Among persons taking ART, 76% had never been troubled by ART side effects during the past 30 days; 14% had rarely been troubled. Among persons who had ever missed a dose, the most common reasons given for not taking one’s most recently missed ART dose were forgetting (60%), a change in one’s daily routine or being out of town (40%), and falling asleep early or oversleeping (35%) (Figure 8).
Clinical Characteristics by Selected Populations
The estimated prevalence of ART prescription documented in a medical record was 83% among males and 83% among females (Table 9). An estimated 80% of Blacks or African Americans were prescribed ART, compared with 86% of Hispanics or Latinos and 85% of Whites. The estimated prevalence of ART prescription was 76% among persons aged 18 to 29 years and 85% among those aged 50 years or older.
The estimated prevalence of sustained viral suppression was 62% among males and 59% among females. An estimated 56% of Blacks or African Americans had sustained viral suppression, compared with 67% of Hispanics or Latinos and 66% of Whites. The estimated prevalence of sustained viral suppression was 49% among persons aged 18 to 29 years and 67% among those aged 50 years or older.
Depression and Substance Use
The estimated prevalence of major or other depression in the past 2 weeks based on the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-8) algorithm [11] was 16%, including 9% with major depression (Figure 9; Table 10). Based on the total PHQ-8 symptom score (see the appendix), an estimated 13% of persons had moderate or severe depression. The estimated prevalence of mild, moderate, or severe anxiety in the past 2 weeks based on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD-7) [12] was 21%, including 7% with severe anxiety.
The estimated prevalence of current smoking was 32%: 26% of persons smoked daily, 3% weekly, 1% monthly, and 2% less than monthly (Figure 10; Table 11). The estimated prevalence of alcohol use was 61%: 6% of persons drank alcohol daily, 18% weekly, 12% monthly, and 25% less than monthly (Figure 10; Table 12). An estimated 15% of persons engaged in binge drinking during the past 30 days.
An estimated 32% of persons used noninjection drugs for nonmedical purposes (Table 13). In total, an estimated 29% used marijuana, 7% used poppers (amyl nitrite), 6% used cocaine, 5% used methamphetamines, 4% used club drugs, 3% used crack, and 3% used prescription opioids. An estimated 3% of persons used injection drugs for nonmedical purposes (Table 14). In total, an estimated 2% injected methamphetamines and 1% injected heroin.
Gynecologic and Reproductive Health
Among females, 88% reported receiving a Papanicolaou (Pap) test in the past 3 years (Figure 11; Table 15). An estimated 28% of females reported being pregnant at least once since receiving an HIV diagnosis.
Sexual Behavior
An estimated 35% of men had receptive anal sex with men, 32% had insertive anal sex with men, and 18% had vaginal sex (Table 16). An estimated 39% of men did not have vaginal or anal sex. Among women, an estimated 5% had receptive anal sex, 50% had vaginal sex, and 50% did not have vaginal or anal sex. Among transgender persons, 75% had vaginal or anal sex (Table 17).
Among men who had sex with men, an estimated 9% engaged in high-risk sex, compared with 5% of men who had sex only with women and 7% of women who had sex with men (Figure 12; Table 18).
In terms of prevention strategies among sexually active persons, an estimated 63% of men who had sex with men engaged in sex and had sustained viral suppression, 56% had condom-protected sex, 17% had condomless sex with a partner on preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and 57% had sex with a person with HIV (Figure 13; Table 18). Among sexually active men who had sex only with women, 60% engaged in sex and had sustained viral suppression, 69% had condom-protected sex, 4% had condomless sex with a partner on PrEP, and 20% had sex with a person with HIV. Among sexually active women who had sex with men, 56% engaged in sex and had sustained viral suppression, 54% had condom-protected sex, 2% had condomless sex with a partner on PrEP, and 23% had sex with a person with HIV.
Met and Unmet Need for Ancillary Services
Among all HIV support services, the most commonly reported service received in the 12 months before interview was HIV case management (57%); estimated unmet need for HIV case management services was 7% (Figure 14; Table 19). Of all non-HIV medical care services, the most commonly reported service received was dental care (61%); 22% reported an unmet need for dental care. Among all subsistence services, the most commonly reported services received were obtained through the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) or Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) (37%); unmet need for SNAP or WIC services was 11%.
Physical Violence and Forced Sex
An estimated 25% of persons had ever been physically hurt by a romantic or sexual partner, including 4% who experienced this in the past 12 months (Figure 15; Table 20). An estimated 17% of persons had ever been threatened with harm or physically forced to have unwanted sex, including 1% who experienced this in the past 12 months.
Prevention Activities
An estimated 61% of persons received counseling from a physician, nurse, or other health care worker about HIV and STD risk reduction; 32% had a one-on-one conversation with an outreach worker, a counselor, or a prevention program worker about prevention; and 12% participated in a small-group session (excluding discussions with friends) to discuss the prevention of HIV and other STDs (Figure 16; Table 21). An estimated 46% of persons received free condoms from various organizations.
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
|