| |
High frequency of memory stem cells with a distinct gene signature in HIV patients with treatment interruption
|
| |
| |
Download the PDF here
----------------------
SMART Yields More Reasons To Shun Drug Breaks
SMART Study Strategies for Management of Antiretroviral Therapy Study
Effects of alternate treatment protocols (discontinuation vs viral suppression) on the incidence of electrocardiographic abnormalities among HIV-infected adults in the SMART trial - (08/06/07)
DC patients had HIV RNA levels >400 copies/mL for most of the follow-up time when their CD4+ cell counts were ⩾350 cells/μL, and this uncontrolled viral replication even at these higher CD4+ cell counts was associated with an increased risk of OD/death.
https://academic.oup.com/jid/article/197/8/1145/903025
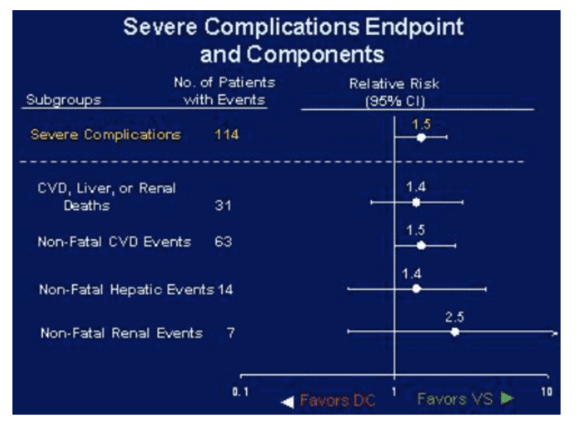
The results of the smart study showed that it compared with ct, was associated with increased risks of aids or death, serious aids-defining events, and severe complications
https://www.prn.org/images/pdfs/68_siegal_lawrence.pdf
-----------------------------
High frequency of memory stem cells with a distinct gene signature in HIV patients with treatment interruption
First published: 28 February 2023
Meenakshi Sachdeva1 , Aman Sharma2 , Sunil K Arora1,3 *
1 Department of Translational and Regenerative medicine, Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh, India.
Abstract
Reservoirs of HIV remain a major obstacle to the complete eradication of virus despite regular anti-retroviral therapy (ART). Memory stem cells (Tscm), one of the major reservoirs are relatively less studied owing to their presence in lower numbers and inaccessible anatomical locations. We have evaluated the molecular characteristics of Tscms in patients with ART interruption (n=15) versus patients on uninterrupted ART (n=12) using flowcytometry. RNA sequencing was done in the sorted Tscms to study the differential gene expression.
Patients with ART interruption had significantly lower baseline CD4+T-cell counts and high viral loads as compared to patients on ART. The former group had significantly higher frequency of CD4+ and CD8+Tscms with a higher expression of PD-1 on CD8+Tscms. The transcriptome profile of Tscm was significantly different amongst the patient groups. The main pathways were cellular and metabolic pathways, cellular development pathways, cell differentiation and negative regulation of cellular migratory pathways.
An increased yet dysfunctional CD8+ memory stem cells describes HIV-1 infected patients with break in ART and a distinct transcriptional signature of CD4+ Tscm as compared to those of patients on ART. A more detailed understanding of biology and dynamics of Tscm in future studies is warranted. Strategies to improve the functionality of the CD8+ Tscm will help these patients to tackle the outburst of viral replication that occur after the cessation of therapy.
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
|